Hsl7p, a negative regulator of Ste20p protein kinase in the Saccharomyces cerevisiae filamentous growth-signaling pathway
- PMID: 10411908
- PMCID: PMC17549
- DOI: 10.1073/pnas.96.15.8522
Hsl7p, a negative regulator of Ste20p protein kinase in the Saccharomyces cerevisiae filamentous growth-signaling pathway
Abstract
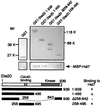
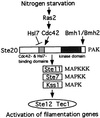
In the budding yeast, Saccharomyces cerevisiae, protein kinases Ste20p (p21(Cdc42p/Rac)-activated kinase), Ste11p [mitogen-activated protein kinase (MAPK) kinase kinase], Ste7p (MAPK kinase), Fus3p, and Kss1p (MAPKs) are utilized for haploid mating, invasive growth, and diploid filamentous growth. Members of the highly conserved Ste20p/p65(PAK) protein kinase family regulate MAPK signal transduction pathways from yeast to man. We describe here a potent negative regulator of Ste20p in the yeast filamentous growth-signaling pathway. We identified a mutant, hsl7, that exhibits filamentous growth on rich medium. Hsl7p belongs to a highly conserved protein family in eukaryotes. Hsl7p associates with the noncatalytic region within the amino-terminal half of Ste20p as well as Cdc42p. Deletions of HSL7 in haploid and diploid strains led to cell elongation and enhancement of both haploid invasive growth and diploid pseudohyphal growth. However, deletions of STE20 in haploid and diploid greatly diminished these hsl7-associated phenotypes. In addition, overexpression of HSL7 inhibited pseudohyphal growth. Thus, Hsl7p may inhibit the activity of Ste20p in the S. cerevisiae filamentous growth-signaling pathway. Our genetic analyses suggest the possibility that Cdc42p and Hsl7p compete for binding to Ste20p for pseudohyphal development when starved for nitrogen.
Figures




Similar articles
-
Functional characterization of the Cdc42p binding domain of yeast Ste20p protein kinase.EMBO J. 1997 Jan 2;16(1):83-97. doi: 10.1093/emboj/16.1.83. EMBO J. 1997. PMID: 9009270 Free PMC article.
-
Crosstalk between the Ras2p-controlled mitogen-activated protein kinase and cAMP pathways during invasive growth of Saccharomyces cerevisiae.Mol Biol Cell. 1999 May;10(5):1325-35. doi: 10.1091/mbc.10.5.1325. Mol Biol Cell. 1999. PMID: 10233147 Free PMC article.
-
Ras2 signals via the Cdc42/Ste20/mitogen-activated protein kinase module to induce filamentous growth in Saccharomyces cerevisiae.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1996 May 28;93(11):5352-6. doi: 10.1073/pnas.93.11.5352. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1996. PMID: 8643578 Free PMC article.
-
Regulation of phosphorylation pathways by p21 GTPases. The p21 Ras-related Rho subfamily and its role in phosphorylation signalling pathways.Eur J Biochem. 1996 Dec 1;242(2):171-85. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1996.0171r.x. Eur J Biochem. 1996. PMID: 8973630 Review.
-
A conserved Gbeta binding (GBB) sequence motif in Ste20p/PAK family protein kinases.Biol Chem. 2000 May-Jun;381(5-6):427-31. doi: 10.1515/BC.2000.055. Biol Chem. 2000. PMID: 10937873 Review.
Cited by
-
Defects in protein glycosylation cause SHO1-dependent activation of a STE12 signaling pathway in yeast.Genetics. 2000 Jul;155(3):1005-18. doi: 10.1093/genetics/155.3.1005. Genetics. 2000. PMID: 10880465 Free PMC article.
-
A role for the Swe1 checkpoint kinase during filamentous growth of Saccharomyces cerevisiae.Genetics. 2001 Jun;158(2):549-62. doi: 10.1093/genetics/158.2.549. Genetics. 2001. PMID: 11404321 Free PMC article.
-
Negative regulation of transcription by the type II arginine methyltransferase PRMT5.EMBO Rep. 2002 Jul;3(7):641-5. doi: 10.1093/embo-reports/kvf136. EMBO Rep. 2002. PMID: 12101096 Free PMC article.
-
Mechanisms regulating the protein kinases of Saccharomyces cerevisiae.Eukaryot Cell. 2007 Apr;6(4):571-83. doi: 10.1128/EC.00026-07. Epub 2007 Mar 2. Eukaryot Cell. 2007. PMID: 17337635 Free PMC article. Review. No abstract available.
-
Glucose depletion causes haploid invasive growth in yeast.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2000 Dec 5;97(25):13619-24. doi: 10.1073/pnas.240345197. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2000. PMID: 11095711 Free PMC article.
References
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
- Actions
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

