One lyn molecule is sufficient to initiate phosphorylation of aggregated high-affinity IgE receptors
- PMID: 10411924
- PMCID: PMC17565
- DOI: 10.1073/pnas.96.15.8615
One lyn molecule is sufficient to initiate phosphorylation of aggregated high-affinity IgE receptors
Abstract
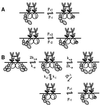
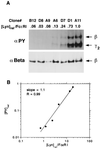
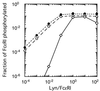
In response to antigenic stimuli, the multisubunit immune recognition receptors become aggregated and then phosphorylated on their cytoplasmic tyrosines. For the clonotypic receptors of B and T cells and for Fc receptors such as the high-affinity receptor for IgE (FcepsilonRI), a Src family kinase initiates this phosphorylation. We ask whether aggregation of the initiating kinase itself is required for signal transduction or whether, alternatively, a single associated kinase molecule can phosphorylate the receptors in an aggregate. We formulate the alternative molecular mechanisms mathematically and compare predictions with experimental findings on FcepsilonRI-bearing cells expressing varying amounts of the transfected Src family kinase Lyn. The data are consistent with the requirement of only a single Lyn molecule per FcepsilonRI aggregate to initiate signaling and are inconsistent with a mechanism requiring more than one Lyn molecule.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Rethinking the role of Src family protein tyrosine kinases in the allergic response: new insights on the functional coupling of the high affinity IgE receptor.Immunol Res. 2004;30(2):241-53. doi: 10.1385/ir:30:2:241. Immunol Res. 2004. PMID: 15477664 Review.
-
The unique domain as the site on Lyn kinase for its constitutive association with the high affinity receptor for IgE.J Biol Chem. 1997 Sep 19;272(38):24072-80. doi: 10.1074/jbc.272.38.24072. J Biol Chem. 1997. PMID: 9295361
-
Structure-function analysis of Lyn kinase association with lipid rafts and initiation of early signaling events after Fcepsilon receptor I aggregation.Mol Cell Biol. 2001 Dec;21(24):8318-28. doi: 10.1128/MCB.21.24.8318-8328.2001. Mol Cell Biol. 2001. PMID: 11713268 Free PMC article.
-
Aggregation of the high-affinity IgE receptor and enhanced activity of p53/56lyn protein-tyrosine kinase.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1994 Nov 8;91(23):11251-5. doi: 10.1073/pnas.91.23.11251. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1994. PMID: 7526394 Free PMC article.
-
The role of Src family kinases in mast cell effector function.Novartis Found Symp. 2005;271:39-47; discussion 47-53, 95-9. Novartis Found Symp. 2005. PMID: 16605127 Review.
Cited by
-
Cholesterol deficiency in a mouse model of Smith-Lemli-Opitz syndrome reveals increased mast cell responsiveness.J Exp Med. 2006 May 15;203(5):1161-71. doi: 10.1084/jem.20051701. Epub 2006 Apr 17. J Exp Med. 2006. PMID: 16618793 Free PMC article.
-
Spatial Stochastic Model of the Pre-B Cell Receptor.IEEE/ACM Trans Comput Biol Bioinform. 2023 Jan-Feb;20(1):683-693. doi: 10.1109/TCBB.2022.3166149. Epub 2023 Feb 3. IEEE/ACM Trans Comput Biol Bioinform. 2023. PMID: 35482702 Free PMC article.
-
Adapters in the organization of mast cell signaling.Immunol Rev. 2009 Nov;232(1):195-217. doi: 10.1111/j.1600-065X.2009.00834.x. Immunol Rev. 2009. PMID: 19909365 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Rethinking the role of Src family protein tyrosine kinases in the allergic response: new insights on the functional coupling of the high affinity IgE receptor.Immunol Res. 2004;30(2):241-53. doi: 10.1385/ir:30:2:241. Immunol Res. 2004. PMID: 15477664 Review.
-
Spatial requirements for ITAM signaling in an intracellular natural killer cell model membrane.Biochim Biophys Acta Gen Subj. 2022 Nov;1866(11):130221. doi: 10.1016/j.bbagen.2022.130221. Epub 2022 Aug 3. Biochim Biophys Acta Gen Subj. 2022. PMID: 35933027 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Thomas S M, Brugge J S. Annu Rev Cell Dev Biol. 1997;13:513–609. - PubMed
-
- Paolini R, Jouvin M-H, Kinet J-P. Nature (London) 1991;353:855–858. - PubMed
-
- Eiseman E, Bolen J B. Nature (London) 1992;355:78–80. - PubMed
-
- Benhamou M. In: IgE Receptor (FcɛRI) Function in Mast Cells and Basophils, Hamaway M M, editor. Austin, TX: Landes; 1997. pp. 33–54.
-
- Metzger H, Alcarez G, Hohman R, Kinet J-P, Pribluda V, Quarto R. Annu Rev Immunol. 1986;4:419–470. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

