Long-term regulated expression of growth hormone in mice after intramuscular gene transfer
- PMID: 10411931
- PMCID: PMC17572
- DOI: 10.1073/pnas.96.15.8657
Long-term regulated expression of growth hormone in mice after intramuscular gene transfer
Abstract
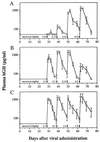
Effective delivery of secreted proteins by gene therapy will require a vector that directs stable delivery of a transgene and a regulatory system that permits pharmacologic control over the level and kinetics of therapeutic protein expression. We previously described a regulatory system that enables transcription of a target gene to be controlled by rapamycin, an orally bioavailable drug. Here we demonstrate in vivo regulation of gene expression after intramuscular injection of two separate adenovirus or adeno-associated virus (AAV) vectors, one encoding an inducible human growth hormone (hGH) target gene, and the other a bipartite rapamycin-regulated transcription factor. Upon delivery of either vector system into immunodeficient mice, basal plasma hGH expression was undetectable and was induced to high levels after administration of rapamycin. The precise level and duration of hGH expression could be controlled by the rapamycin dosing regimen. Equivalent profiles of induction were observed after repeated administration of single doses of rapamycin over many months. AAV conferred stable expression of regulated hGH in both immunocompetent and immunodeficient mice, whereas adenovirus-directed hGH expression quickly extinguished in immunocompetent animals. These studies demonstrate that the rapamycin-based regulatory system, delivered intramuscularly by AAV, fulfills many of the conditions necessary for the safe and effective delivery of therapeutic proteins by gene therapy.
Figures


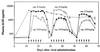

Similar articles
-
Long-term pharmacologically regulated expression of erythropoietin in primates following AAV-mediated gene transfer.Blood. 2005 Feb 15;105(4):1424-30. doi: 10.1182/blood-2004-06-2501. Epub 2004 Oct 26. Blood. 2005. PMID: 15507527
-
Rapamycin-regulated control of antiangiogenic tumor therapy following rAAV-mediated gene transfer.Mol Ther. 2007 May;15(5):912-20. doi: 10.1038/mt.sj.6300079. Epub 2007 Jan 23. Mol Ther. 2007. PMID: 17245354
-
Regulated delivery of therapeutic proteins after in vivo somatic cell gene transfer.Science. 1999 Jan 1;283(5398):88-91. doi: 10.1126/science.283.5398.88. Science. 1999. PMID: 9872748
-
Dimerizer-regulated gene expression.Curr Opin Biotechnol. 2002 Oct;13(5):459-67. doi: 10.1016/s0958-1669(02)00373-7. Curr Opin Biotechnol. 2002. PMID: 12459338 Review.
-
Animal models for growth hormone gene therapy.Curr Gene Ther. 2005 Oct;5(5):493-509. doi: 10.2174/156652305774329258. Curr Gene Ther. 2005. PMID: 16250890 Review.
Cited by
-
A microarray gene analysis of peripheral whole blood in normal adult male rats after long-term GH gene therapy.Cell Mol Biol Lett. 2010 Jun;15(2):177-95. doi: 10.2478/s11658-010-0001-9. Epub 2010 Jan 28. Cell Mol Biol Lett. 2010. PMID: 20119855 Free PMC article.
-
The potential of adeno-associated viral vectors for gene delivery to muscle tissue.Expert Opin Drug Deliv. 2014 Mar;11(3):345-364. doi: 10.1517/17425247.2014.871258. Epub 2014 Jan 3. Expert Opin Drug Deliv. 2014. PMID: 24386892 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Enhancing the utility of adeno-associated virus gene transfer through inducible tissue-specific expression.Hum Gene Ther Methods. 2013 Aug;24(4):270-8. doi: 10.1089/hgtb.2012.129. Hum Gene Ther Methods. 2013. PMID: 23895325 Free PMC article.
-
Intravenous AAV8 Encoding Urocortin-2 Increases Function of the Failing Heart in Mice.Hum Gene Ther. 2015 Jun;26(6):347-56. doi: 10.1089/hum.2014.157. Epub 2015 Apr 9. Hum Gene Ther. 2015. PMID: 25760560 Free PMC article.
-
A gene expression system offering multiple levels of regulation: the Dual Drug Control (DDC) system.BMC Biotechnol. 2004 Apr 29;4:9. doi: 10.1186/1472-6750-4-9. BMC Biotechnol. 2004. PMID: 15117411 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Tripathy S K, Black H B, Goldwasser E, Leiden J M. Nat Med. 1996;2:545–550. - PubMed
-
- Svensson E C, Black H B, Dugger D L, Tripathy S K, Goldwasser E, Hao Z, Chu L, Leiden J M. Hum Gene Ther. 1997;8:1797–1806. - PubMed
-
- Monahan P E, Samulski R J, Tazelaar J, Xiao X, Nichols T C, Bellinger D A, Read M S, Walsh C E. Gene Ther. 1998;5:40–49. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

