Local presentation of substrate molecules directs axon specification by cultured hippocampal neurons
- PMID: 10414970
- PMCID: PMC6782837
- DOI: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.19-15-06417.1999
Local presentation of substrate molecules directs axon specification by cultured hippocampal neurons
Abstract
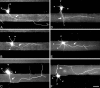
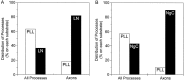
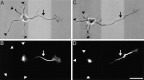
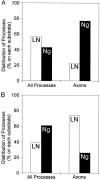
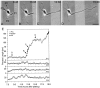
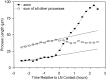
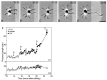
Axon specification is a crucial, early step in neuronal development, but little is known about how this event is controlled in vivo. To test the hypothesis that local presentation of growth-promoting molecules can direct axon specification, we cultured hippocampal neurons on substrates patterned with stripes of poly-L-lysine and either laminin (LN) or the neuron-glia cell adhesion molecule (NgCAM). Although undifferentiated neurites contacted both substrates equally, axons formed preferentially on LN or NgCAM. Time-lapse studies revealed that changes in the growth pattern of a cell indicative of axon specification began almost immediately after the growth cone of one of the neurites of the cell contacted LN or NgCAM. When cells were plated on alternating stripes of LN and NgCAM, cells with their somata on LN usually formed axons on NgCAM, whereas those with somata on NgCAM preferentially formed axons on LN. This suggests that the change from one axon-promoting substrate to another also provides a signal sufficient to specify the axon. These results demonstrate that contact with preferred substrate molecules can govern which neurite becomes the axon and thus direct the development of neuronal polarity.
Figures
References
-
- Bixby JL. Protein kinase C is involved in laminin stimulation of neurite outgrowth. Neuron. 1989;3:287–297. - PubMed
-
- Bottenstein JE. Growth and differentiation of neural cells in defined media. In: Bottenstein JE, Sato G, editors. Cell culture in the neurosciences. Plenum; New York: 1985. pp. 3–44.
-
- Bradke F, Dotti CG. The role of local actin instability in axon formation. Science. 1999;283:1931–1934. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
