ABC of intensive care: outcome data and scoring systems
- PMID: 10417092
- PMCID: PMC1116333
- DOI: 10.1136/bmj.319.7204.241
ABC of intensive care: outcome data and scoring systems
Figures
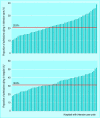
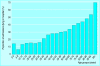
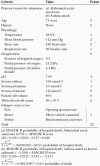

Comment in
-
Mortality prediction model is preferable to APACHE.BMJ. 2000 Mar 11;320(7236):714. BMJ. 2000. PMID: 10710593 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
