Identification of a glycoprotein produced by enterotoxigenic Escherichia coli
- PMID: 10417177
- PMCID: PMC96707
- DOI: 10.1128/IAI.67.8.4084-4091.1999
Identification of a glycoprotein produced by enterotoxigenic Escherichia coli
Abstract
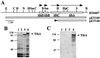
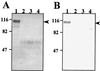
Enterotoxigenic Escherichia coli (ETEC) strain H10407 is capable of invading epithelial cell lines derived from the human ileocecum and colon in vitro. Two separate chromosomally encoded invasion loci (tia and tib) have been cloned from this strain. These loci direct nonadherent and noninvasive laboratory strains of E. coli to adhere to and invade cultured human intestinal epithelial cells. The tib locus directs the synthesis of TibA, a 104-kDa outer membrane protein that is directly correlated with the adherence and invasion phenotypes. TibA is synthesized as a 100-kDa precursor (preTibA) that must be modified for biological activity. Outer membranes of recombinant E. coli expressing TibA or preTibA were separated by sodium dodecyl sulfate-polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis and blotted to nitrocellulose. The presence of glycoproteins was detected by oxidization of carbohydrates with periodate and labeling with hydrazide-conjugated digoxigenin. Only TibA could be detected as a glycoprotein. Complementation experiments with tib deletion mutants of ETEC strain H10407 demonstrate that the TibA glycoprotein is expressed in H10407, that the entire tib locus is required for TibA synthesis, and that TibA is the only glycoprotein produced by H10407. Protease treatment of intact H10407 cells removes the carbohydrates on TibA, suggesting that they are surface exposed. TibA shows homology with AIDA-I from diffuse-adhering E. coli and with pertactin precursor from Bordetella pertussis. Both pertactin and AIDA-I are members of the autotransporter family of outer membrane proteins and are afimbrial adhesins that play an important role in the virulence of these organisms. Analysis of the predicted TibA amino acid sequence indicates that TibA is also an autotransporter. Analysis of the tib locus DNA sequence revealed an open reading frame with similarity to RfaQ, a glycosyltransferase. The product of this tib locus open reading frame is proposed to be responsible for TibA modification. These results suggest that TibA glycoprotein acts as an adhesin that may participate in the disease process.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Epithelial cell invasion and adherence directed by the enterotoxigenic Escherichia coli tib locus is associated with a 104-kilodalton outer membrane protein.Infect Immun. 1994 Aug;62(8):3463-71. doi: 10.1128/iai.62.8.3463-3471.1994. Infect Immun. 1994. PMID: 8039917 Free PMC article.
-
Enterotoxigenic Escherichia coli TibA glycoprotein adheres to human intestine epithelial cells.Infect Immun. 2001 Jan;69(1):52-7. doi: 10.1128/IAI.69.1.52-57.2001. Infect Immun. 2001. PMID: 11119488 Free PMC article.
-
Molecular characterization of the tia invasion locus from enterotoxigenic Escherichia coli.Infect Immun. 1996 Jun;64(6):2256-65. doi: 10.1128/iai.64.6.2256-2265.1996. Infect Immun. 1996. PMID: 8675335 Free PMC article.
-
Phase-variable outer membrane proteins in Escherichia coli.FEMS Immunol Med Microbiol. 1996 Dec 1;16(2):63-76. doi: 10.1111/j.1574-695X.1996.tb00124.x. FEMS Immunol Med Microbiol. 1996. PMID: 8988388 Review.
-
Self-associating autotransporters, SAATs: functional and structural similarities.Int J Med Microbiol. 2006 Aug;296(4-5):187-95. doi: 10.1016/j.ijmm.2005.10.002. Int J Med Microbiol. 2006. PMID: 16600681 Review.
Cited by
-
Molecular characterization of enterotoxigenic Escherichia coli isolates recovered from children with diarrhea during a 4-year period (2007 to 2010) in Bolivia.J Clin Microbiol. 2013 Apr;51(4):1219-25. doi: 10.1128/JCM.02971-12. Epub 2013 Feb 6. J Clin Microbiol. 2013. PMID: 23390275 Free PMC article.
-
O-linked glycosylation ensures the normal conformation of the autotransporter adhesin involved in diffuse adherence.J Bacteriol. 2007 Dec;189(24):8880-9. doi: 10.1128/JB.00969-07. Epub 2007 Oct 19. J Bacteriol. 2007. PMID: 17951390 Free PMC article.
-
Differentially expressed and secreted major immunoreactive protein orthologs of Ehrlichia canis and E. chaffeensis elicit early antibody responses to epitopes on glycosylated tandem repeats.Infect Immun. 2006 Jan;74(1):711-20. doi: 10.1128/IAI.74.1.711-720.2006. Infect Immun. 2006. PMID: 16369028 Free PMC article.
-
Molecular analysis of an alternative N-glycosylation machinery by functional transfer from Actinobacillus pleuropneumoniae to Escherichia coli.J Biol Chem. 2014 Jan 24;289(4):2170-9. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M113.524462. Epub 2013 Nov 25. J Biol Chem. 2014. PMID: 24275653 Free PMC article.
-
Glycosylation of Twisted Gastrulation is Required for BMP Binding and Activity during Craniofacial Development.Front Physiol. 2011 Sep 12;2:59. doi: 10.3389/fphys.2011.00059. eCollection 2011. Front Physiol. 2011. PMID: 21941513 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Benz I, Schmidt M A. AIDA-I, the adhesin involved in diffuse adherence of the diarrhoeagenic Escherichia coli strain 2787 (O126:H27), is synthesized via a precursor molecule. Mol Microbiol. 1992;6:1539–1546. - PubMed
-
- Black R. Epidemiology of diarrhoeal disease: implications for control by vaccines. Vaccine. 1993;11:100–106. - PubMed
-
- Boyer H W, Rouland-Dussoix D. A complementation analysis of the restriction and modification of DNA in Escherichia coli. J Mol Biol. 1969;41:459–472. - PubMed
-
- Bradford M M. A rapid and sensitive method for the quantitation of microgram quantities of protein utilizing the principle of protein-dye binding. Anal Biochem. 1976;72:248–254. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
- Actions
- Actions
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials

