Cloning, sequencing, and characterization of the cgmB gene of Sinorhizobium meliloti involved in cyclic beta-glucan biosynthesis
- PMID: 10419956
- PMCID: PMC103589
- DOI: 10.1128/JB.181.15.4576-4583.1999
Cloning, sequencing, and characterization of the cgmB gene of Sinorhizobium meliloti involved in cyclic beta-glucan biosynthesis
Abstract
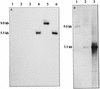
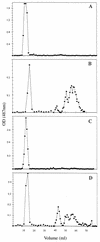
Periplasmic cyclic beta-glucans of Rhizobium species provide important functions during plant infection and hypo-osmotic adaptation. In Sinorhizobium meliloti (also known as Rhizobium meliloti), these molecules are highly modified with phosphoglycerol and succinyl substituents. We have previously identified an S. meliloti Tn5 insertion mutant, S9, which is specifically impaired in its ability to transfer phosphoglycerol substituents to the cyclic beta-glucan backbone (M. W. Breedveld, J. A. Hadley, and K. J. Miller, J. Bacteriol. 177:6346-6351, 1995). In the present study, we have cloned, sequenced, and characterized this mutation at the molecular level. By using the Tn5 flanking sequences (amplified by inverse PCR) as a probe, an S. meliloti genomic library was screened, and two overlapping cosmid clones which functionally complement S9 were isolated. A 3.1-kb HindIII-EcoRI fragment found in both cosmids was shown to fully complement mutant S9. Furthermore, when a plasmid containing this 3.1-kb fragment was used to transform Rhizobium leguminosarum bv. trifolii TA-1JH, a strain which normally synthesizes only neutral cyclic beta-glucans, anionic glucans containing phosphoglycerol substituents were produced, consistent with the functional expression of an S. meliloti phosphoglycerol transferase gene. Sequence analysis revealed the presence of two major, overlapping open reading frames within the 3.1-kb fragment. Primer extension analysis revealed that one of these open reading frames, ORF1, was transcribed and its transcription was osmotically regulated. This novel locus of S. meliloti is designated the cgm (cyclic glucan modification) locus, and the product encoded by ORF1 is referred to as CgmB.
Figures



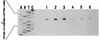

References
-
- Altschul S F, Gish W, Miller W, Myers E W, Lipman D J. Basic local alignment search tool. J Mol Biol. 1990;215:403–410. - PubMed
-
- Anderson M L M, Young B D. Quantitative filter hybridization. In: Hames B D, Higgins S J, editors. Nucleic acid hybridization: a practical approach. Oxford, England: IRL Press; 1985. pp. 73–111.
-
- Becker A A, Kleickmann A A, Arnold W, Puhler A. Analysis of the Rhizobium meliloti exoH/exoK/exoL fragment: ExoK shows homology to excreted endo-beta-1,3-1,4-glucanases and ExoH resembles membrane proteins. Mol Gen Genet. 1993;238:145–154. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
- Actions
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

