Signaling to actin dynamics
- PMID: 10427083
- PMCID: PMC2156183
- DOI: 10.1083/jcb.146.2.267
Signaling to actin dynamics
Figures
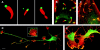
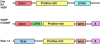

References
-
- Aspenstrom P., Lindberg U., Hall A. Two GTPases, Cdc42 and Rac, bind directly to a protein implicated in the immunodeficiency disorder Wiskott-Aldrich Syndrome. Curr. Biol. 1996;6:70–75. - PubMed
-
- Aszodi A., Pfeifer A., Ahmad M., Glauner M., Zhou X.H., Ny L., Andersson K.E., Kehrel B., Offermanns S., Fassler R. The vasodilator-stimulated phosphoprotein (VASP) is involved in cGMP- and cAMP-mediated inhibition of agonist-induced platelet aggregation, but is dispensable for smooth muscle function. EMBO (Eur. Mol. Biol. Organ.) J. 1999;18:37–48. - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

