A novel type of AmpC beta-lactamase, ACC-1, produced by a Klebsiella pneumoniae strain causing nosocomial pneumonia
- PMID: 10428914
- PMCID: PMC89392
- DOI: 10.1128/AAC.43.8.1924
A novel type of AmpC beta-lactamase, ACC-1, produced by a Klebsiella pneumoniae strain causing nosocomial pneumonia
Abstract
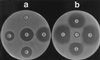
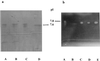
A Klebsiella pneumoniae strain resistant to oxyimino cephalosporins was cultured from respiratory secretions of a patient suffering from nosocomial pneumonia in Kiel, Germany, in 1997. The isolate harbors a bla resistance gene located on a transmissible plasmid. An Escherichia coli transconjugant produces a beta-lactamase with an isoelectric point of 7.7 and a resistance phenotype characteristic of an AmpC (class 1) beta-lactamase except for low MICs of cephamycins. The bla gene was cloned and sequenced. It encodes a protein of 386 amino acids with the active site serine of the S-X-X-K motif at position 64, as is characteristic for class C beta-lactamases. Multiple alignment of the deduced amino acid sequence with 21 other AmpC beta-lactamases demonstrates only very distant homology, reaching at maximum 52.3% identity for the chromosomal AmpC beta-lactamase of Serratia marcescens SR50. The beta-lactamase of K. pneumoniae KUS represents a new type of AmpC-class enzyme, for which we propose the designation ACC-1 (Ambler class C-1).
Figures


References
-
- Barnaud G, Arlet G, Danglot C, Philippon A. Cloning and sequencing of the gene encoding the AmpC β-lactamase of Morganella morganii. FEMS Microbiol Lett. 1997;148:15–20. - PubMed
-
- Bauernfeind A, Chong Y, Lee K. Plasmid-encoded AmpC β-lactamases: how far have we gone 10 years after their discovery? Yonsei Med J. 1998;39:520–525. - PubMed
-
- Bauernfeind A, Chong Y, Schweighart S. Extended broad spectrum β-lactamase in Klebsiella pneumoniae including resistance to cephamycins. Infection. 1989;17:316–321. - PubMed
-
- Bauernfeind A, Grimm H, Schweighart S. A new plasmidic cefotaximase in a clinical isolate of Escherichia coli. Infection. 1990;18:294–298. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
- Actions
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

