B cell development in the spleen takes place in discrete steps and is determined by the quality of B cell receptor-derived signals
- PMID: 10429672
- PMCID: PMC2195560
- DOI: 10.1084/jem.190.1.75
B cell development in the spleen takes place in discrete steps and is determined by the quality of B cell receptor-derived signals
Abstract
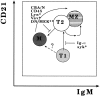
Only mature B lymphocytes can enter the lymphoid follicles of spleen and lymph nodes and thus efficiently participate in the immune response. Mature, long-lived B lymphocytes derive from short-lived precursors generated in the bone marrow. We show that selection into the mature pool is an active process and takes place in the spleen. Two populations of splenic B cells were identified as precursors for mature B cells. Transitional B cells of type 1 (T1) are recent immigrants from the bone marrow. They develop into the transitional B cells of type 2 (T2), which are cycling and found exclusively in the primary follicles of the spleen. Mature B cells can be generated from T1 or T2 B cells. Mice with genetic deletions of elements participating in the B cell receptor signaling cascade display developmental arrest at the T1 or T2 stage. The analysis of these defects showed that the development of T2 and mature B cells from T1 precursors requires defined qualitative and quantitative signals derived from the B cell receptor and that the induction of longevity and maturation requires different signals.
Figures
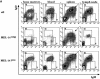







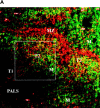



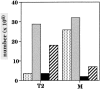
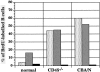



References
-
- Rolink A., Melchers F. B-cell development in the mouse. Immunol. Lett. 1996;54:157–161. - PubMed
-
- Reth M. The B-cell antigen receptor complex and co-receptors. Immunol. Today. 1995;16:310–313. - PubMed
-
- Jacobsen K., Osmond D.G. Microenvironmental organization and stromal cell associations of B lymphocyte precursor cells in mouse bone marrow. Eur. J. Immunol. 1990;20:2395–2404. - PubMed
-
- Allman D.M., Ferguson S.E., Lentz V.M., Cancro M.P. Peripheral B cell maturation. II. Heat-stable antigen(hi) splenic B cells are an immature developmental intermediate in the production of long-lived marrow-derived B cells. J. Immunol. 1993;151:4431–4444. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

