Influence of the high density lipoprotein receptor SR-BI on reproductive and cardiovascular pathophysiology
- PMID: 10430941
- PMCID: PMC17781
- DOI: 10.1073/pnas.96.16.9322
Influence of the high density lipoprotein receptor SR-BI on reproductive and cardiovascular pathophysiology
Abstract
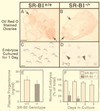
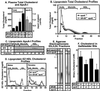
The high density lipoprotein (HDL) receptor SR-BI (scavenger receptor class B type I) mediates the selective uptake of plasma HDL cholesterol by the liver and steroidogenic tissues. As a consequence, SR-BI can influence plasma HDL cholesterol levels, HDL structure, biliary cholesterol concentrations, and the uptake, storage, and utilization of cholesterol by steroid hormone-producing cells. Here we used homozygous null SR-BI knockout mice to show that SR-BI is required for maintaining normal biliary cholesterol levels, oocyte development, and female fertility. We also used SR-BI/apolipoprotein E double homozygous knockout mice to show that SR-BI can protect against early-onset atherosclerosis. Although the mechanisms underlying the effects of SR-BI loss on reproduction and atherosclerosis have not been established, potential causes include changes in (i) plasma lipoprotein levels and/or structure, (ii) cholesterol flux into or out of peripheral tissues (ovary, aortic wall), and (iii) reverse cholesterol transport, as indicated by the significant reduction of gallbladder bile cholesterol levels in SR-BI and SR-BI/apolipoprotein E double knockout mice relative to controls. If SR-BI has similar activities in humans, it may become an attractive target for therapeutic intervention in a variety of diseases.
Figures

References
-
- Gordon D J, Rifkind B M. N Engl J Med. 1989;321:1311–1316. - PubMed
-
- Johnson W J, Mahlberg F H, Rothblat G H, Phillips M C. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1991;1085:273–298. - PubMed
-
- Tall A R. J Lipid Res. 1993;34:1255–1274. - PubMed
-
- Pieters M N, Schouten D, VanBerkel T J C. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1994;1225:125–134. - PubMed
-
- Fielding C J, Fielding P E. J Lipid Res. 1995;36:211–228. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials

