Characterization of beta-adrenoceptor mediated smooth muscle relaxation and the detection of mRNA for beta1-, beta2- and beta3-adrenoceptors in rat ileum
- PMID: 10433503
- PMCID: PMC1566085
- DOI: 10.1038/sj.bjp.0702605
Characterization of beta-adrenoceptor mediated smooth muscle relaxation and the detection of mRNA for beta1-, beta2- and beta3-adrenoceptors in rat ileum
Abstract
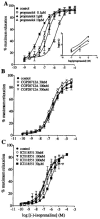
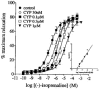
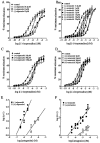
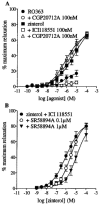
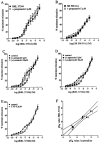
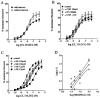
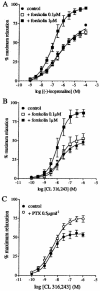
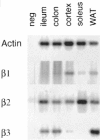
1. Functional and molecular approaches were used to characterize the beta-AR subtypes mediating relaxation of rat ileal smooth muscle. 2. In functional studies, (-)-isoprenaline relaxation was unchanged by CGP20712A (beta1-AR antagonist) or ICI118551 (beta2-AR antagonist) but shifted by propranolol (pKB=6.69). (+/-)-Cyanopindolol, CGP12177 and ICID7114 did not cause relaxation but antagonized (-)-isoprenaline relaxation. 3. BRL37344 (beta3-AR agonist) caused biphasic relaxation. The high affinity component was shifted with low affinity by propranolol, (+/-)-cyanopindolol, tertatolol and alprenolol. CL316243 (beta3-AR agonist) relaxation was unaffected by CGP20712A or ICI118551 but blocked by SR58894A (beta3-AR antagonist; pA2 = 7.80). Enhanced relaxation after exposure to forskolin and pertussis toxin showed that beta3-AR relaxation can be altered by manipulation of components of the adenylate cyclase signalling pathway. 4. The beta-AR agonist RO363 relaxed the ileum (pEC50=6.18) and was blocked by CGP20712A. Relaxation by the beta2-AR agonist zinterol (pEC50=5.71) was blocked by SR58894A but not by ICI118551. 5. In rat ileum, beta1-, beta2- and beta3-AR mRNA was detected. Comparison of tissues showed that beta3-AR mRNA expression was greatest in WAT>colon=ileum >cerebral cortex>soleus; beta1-AR mRNA was most abundant in cerebral cortex > WAT > ileum = colon > soleus; beta2-AR mRNA was expressed in soleus > WAT > ileum = colon > cerebral cortex. 6. These results show that beta3-ARs are the predominant beta-AR subtype mediating rat ileal relaxation while beta1-ARs may produce a small relaxation. The beta2-AR agonist zinterol produces relaxation through beta3-ARs and there was no evidence for the involvement of beta2-ARs in relaxation despite the detection of beta2-AR mRNA.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Differential regulation of beta3-adrenoceptors in gut and adipose tissue of genetically obese (ob/ob) C57BL/6J-mice.Br J Pharmacol. 1998 Jun;124(4):763-71. doi: 10.1038/sj.bjp.0701867. Br J Pharmacol. 1998. PMID: 9690869 Free PMC article.
-
Functional and molecular biological evidence for a possible beta3-adrenoceptor in the human detrusor muscle.Br J Pharmacol. 1999 Feb;126(3):819-25. doi: 10.1038/sj.bjp.0702358. Br J Pharmacol. 1999. PMID: 10188996 Free PMC article.
-
Beta2- and beta3-adrenoceptors activate glucose uptake in chick astrocytes by distinct mechanisms: a mechanism for memory enhancement?J Neurochem. 2007 Nov;103(3):997-1008. doi: 10.1111/j.1471-4159.2007.04789.x. Epub 2007 Aug 6. J Neurochem. 2007. PMID: 17680985
-
The beta-adrenergic receptors.Herz. 2002 Nov;27(7):683-90. doi: 10.1007/s00059-002-2434-z. Herz. 2002. PMID: 12439640 Review.
-
Beta3-adrenoceptors in human detrusor muscle.Urology. 2002 May;59(5 Suppl 1):25-9. doi: 10.1016/s0090-4295(01)01635-1. Urology. 2002. PMID: 12007519 Review.
Cited by
-
β(3) Receptors: Role in Cardiometabolic Disorders.Ther Adv Endocrinol Metab. 2011 Apr;2(2):65-79. doi: 10.1177/2042018810390259. Ther Adv Endocrinol Metab. 2011. PMID: 23148172 Free PMC article.
-
Pharmacology and immunological actions of a herbal medicine ASHMI on allergic asthma.Phytother Res. 2010 Jul;24(7):1047-55. doi: 10.1002/ptr.3077. Phytother Res. 2010. PMID: 19998324 Free PMC article.
-
The Relaxant Effect of Seed's Essential Oil and Oleo-Gum-Resin of Ferula Assa-Foetida on Isolated Rat's Ileum.Ann Med Health Sci Res. 2014 Mar;4(2):238-41. doi: 10.4103/2141-9248.129050. Ann Med Health Sci Res. 2014. PMID: 24761245 Free PMC article.
-
Relaxant effect of Humulus lupulus extracts on isotonic rat's ileum contractions.Avicenna J Phytomed. 2014 Jan;4(1):53-8. Avicenna J Phytomed. 2014. PMID: 25050301 Free PMC article.
-
Induction of glucose uptake in skeletal muscle by central leptin is mediated by muscle β2-adrenergic receptor but not by AMPK.Sci Rep. 2017 Nov 9;7(1):15141. doi: 10.1038/s41598-017-15548-6. Sci Rep. 2017. PMID: 29123236 Free PMC article.
References
-
- ALTAN V.M., YILDIZOGLU N., OZTURK Y. Decreased gastro-intestinal responses to certain agonists in streptozotocin- and alloxan-diabetic rats in vitro. Pharmacology. 1987;34:143–148. - PubMed
-
- ARCH J.R.S., KAUMANN A. β3- and Atypical β-adrenoceptors. Med. Res. Rev. 1993;13:663–729. - PubMed
-
- BERKOWITZ D.E., NARDONE N.A., SMILEY R.M., PRICE D.T., KREUTTER D.K., FREMEAU R.T., SCHWINN D.A. Distribution of β3-adrenoceptor mRNA in human tissues. Eur. J. Pharmacol. 1995;289:223–228. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

