Role of tachykinin NK2-receptor activation in the allergen-induced late asthmatic reaction, airway hyperreactivity and airway inflammatory cell influx in conscious, unrestrained guinea-pigs
- PMID: 10433512
- PMCID: PMC1566098
- DOI: 10.1038/sj.bjp.0702628
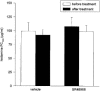
Role of tachykinin NK2-receptor activation in the allergen-induced late asthmatic reaction, airway hyperreactivity and airway inflammatory cell influx in conscious, unrestrained guinea-pigs
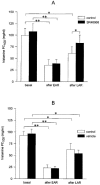
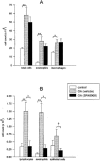
Abstract
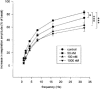
1. In a guinea-pig model of allergic asthma, we investigated the involvement of the tachykinin NK2 receptors in allergen-induced early (EAR) and late (LAR) asthmatic reactions, airway hyperreactivity (AHR) after these reactions and inflammatory cell influx in the airways, using the selective non-peptide NK2 receptor antagonist SR48968. 2. On two different occasions, separated by a 1 week interval, ovalbumin (OA)-sensitized guinea-pigs inhaled either vehicle (3 min) or SR48968 (100 nM, 3 min) at 30 min before as well as at 5.5 h after OA provocation (between the EAR and LAR) in a random crossover design. 3. SR48968 had no significant effect on the EAR, but significantly attenuated the LAR by 44.2+/-16.4% (P<0.05) compared to saline control. 4. The NK2 receptor antagonist did not affect the OA-induced AHR to histamine after the EAR at 5 h after OA challenge (3.59+/-0.59 fold increase in histamine reactivity vs 3.79+/-0.61 fold increase in the controls, NS), but significantly reduced the AHR after the LAR at 23 h after OA challenge (1.59+/-0.24 fold increase vs 1.93+/-0.15 fold increase, respectively, P<0.05). 5. Bronchoalveolar lavage studies performed at 25 h after the second OA provocation showed that SR48968 significantly inhibited the allergen-induced infiltration of neutrophils (P<0.05) and lymphocytes (P<0.01) in the airways. 6. These results indicate that NK2 receptor activation is importantly involved in the development of the allergen-induced late (but not early) asthmatic reaction and late (but not early) AHR to histamine, and that NK2 receptor-mediated infiltration of neutrophils and lymphocytes in the airways may contribute to these effects.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Involvement of tachykinin NK1 receptor in the development of allergen-induced airway hyperreactivity and airway inflammation in conscious, unrestrained guinea pigs.Am J Respir Crit Care Med. 1999 Feb;159(2):423-30. doi: 10.1164/ajrccm.159.2.9804125. Am J Respir Crit Care Med. 1999. PMID: 9927353
-
Role of tachykinin NK1 and NK2 receptors in allergen-induced early and late asthmatic reactions, airway hyperresponsiveness, and airway inflammation in conscious, unrestrained guinea pigs.Clin Exp Allergy. 1999 Jun;29 Suppl 2:48-52. doi: 10.1046/j.1365-2222.1999.00008.x. Clin Exp Allergy. 1999. PMID: 10421822
-
Dual action of iNOS-derived nitric oxide in allergen-induced airway hyperreactivity in conscious, unrestrained guinea pigs.Am J Respir Crit Care Med. 1998 Nov;158(5 Pt 1):1442-9. doi: 10.1164/ajrccm.158.5.9803027. Am J Respir Crit Care Med. 1998. PMID: 9817691
-
Tachykinin NK2 receptors further characterized in the lung with nonpeptide receptor antagonists.Can J Physiol Pharmacol. 1995 Jul;73(7):878-84. doi: 10.1139/y95-121. Can J Physiol Pharmacol. 1995. PMID: 8846425 Review.
-
Allergen-induced late asthmatic responses and increased airway responsiveness.Allergy Proc. 1992 Jan-Feb;13(1):1-2. doi: 10.2500/108854192778879015. Allergy Proc. 1992. PMID: 1577259 Review.
Cited by
-
The role of neuroeffector mechanisms in the pathogenesis of asthma.Curr Allergy Asthma Rep. 2001 Mar;1(2):134-43. doi: 10.1007/s11882-001-0081-8. Curr Allergy Asthma Rep. 2001. PMID: 11899296 Review.
-
Inhibition of airway hyper-responsiveness by TRPV1 antagonists (SB-705498 and PF-04065463) in the unanaesthetized, ovalbumin-sensitized guinea pig.Br J Pharmacol. 2012 Jul;166(6):1822-32. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.2012.01891.x. Br J Pharmacol. 2012. PMID: 22320181 Free PMC article.
References
-
- ADCOCK I.M., PETERS M., GELDER C., SHIRASAKI H., BROWN C.R., BARNES P.J. Increased tachykinin receptor gene expression in asthmatic lung and its modulation by steroids. J. Mol. Endocrinol. 1993;11:1–7. - PubMed
-
- ADVENIER C., LAGENTE V., BOICHOT E. The role of tachykinin receptor antagonists in the prevention of bronchial hyperresponsiveness, airway inflammation and cough. Eur. Respir. J. 1997;10:1892–1906. - PubMed
-
- ADVENIER C., ROUISSI N., NGUYEN Q.T., EMONDS ALT X., BRELIERE J.C., NELIAT G., NALINE E., REGOLI D. Neurokinin A (NK2) receptor revisited with SR 48968, a potent non-peptide antagonist. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 1992;184:1418–1424. - PubMed
-
- BAI T.R., ZHOU D., WEIR T., WALKER B., HEGELE R., HAYASHI S., MCKAY K., BONDY G.P., FONG T. Substance P (NK1)- and neurokinin A (NK2)-receptor gene expression in inflammatory airway diseases. Am. J. Physiol. 1995;269:L309–L317. - PubMed
-
- BARNES P.J. Reactive oxygen species and airway inflammation. Free Radic. Biol. Med. 1990;9:235–243. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

