Vertebrate homologs of Drosophila suppressor of fused interact with the gli family of transcriptional regulators
- PMID: 10433824
- PMCID: PMC4530617
- DOI: 10.1006/dbio.1999.9335
Vertebrate homologs of Drosophila suppressor of fused interact with the gli family of transcriptional regulators
Abstract
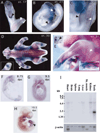
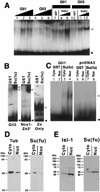
The hedgehog (Hh) signaling pathway is crucial for pattern formation during metazoan development. Although originially characterized in Drosophila, vertebrate homologs have been identified for several, but not all, genes in the pathway. Analysis of mutants in Drosophila demonstrates that Suppressor of fused [Su(fu)] interacts genetically with genes encoding proteins in the Hh signal transduction pathway, and its protein product physically interacts with two of the proteins in the Hh pathway. We report here the molecular cloning and characterization of chicken and mouse homologs of Su(fu). The chick and mouse proteins are 27% identical and 53% similar at the amino acid level to the Drosophila melanogaster and Drosophila virilis proteins. Vertebrate Su(fu) is widely expressed in the developing embryo with higher levels in tissues that are known to be patterned by Hh signaling. The chick Su(fu) protein can physically interact with factors known to function in Hh signal transduction including the Drosophila serine/threonine kinase, Fused, and the vertebrate transcriptional regulators Gli1 and Gli3. This interaction may be significant for transcriptional regulation, as recombinant Su(fu) enhances the ability of Gli proteins to bind DNA in electrophoretic mobility shift assays.
Copyright 1999 Academic Press.
Figures



References
-
- Akiyama H, Shigeno C, Hiraki Y, Shukunami C, Kohno H, Akagi M, Konishi J, Nakamura T. Cloning of a mouse smoothened cDNA and expression patterns of hedgehog signalling molecules during chondrogenesis and cartilage differentiation in clonal mouse EC cells, ATDC5. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 1997;235:142–147. - PubMed
-
- Alcedo J, Ayzenzon M, Von Ohlen T, Noll M, Hooper JE. The Drosophila smoothened gene encodes a seven-pass membrane protein, a putative receptor for the hedgehog signal. Cell. 1996;86:221–232. - PubMed
-
- Alexandre C, Jacinto A, Ingham PW. Transcriptional activation of hedgehog target genes in Drosophila is mediated directly by the cubitus interruptus protein, a member of the GLI family of zinc finger DNA-binding proteins. Genes Dev. 1996;10:2003–2013. - PubMed
-
- Alves G, Limbourg-Bouchon B, Tricoire H, Brissard-Zahraoui J, Lamour-Isnard C, Busson D. Modulation of hedgehog target gene expression by the fused serine-threonine kinase in wing imaginal discs. Mech. Dev. 1998;78:17–31. - PubMed
-
- Aruga J, Nagai T, Tokuyama T, Hayashizaki Y, Okazaki Y, Chapman VM, Mikoshiba K. The mouse zic gene family. Homologues of the Drosophila pair-rule gene odd-paired. J. Biol. Chem. 1996a;271:1043–1047. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

