Tumor-associated transforming growth factor-beta and interleukin-10 contribute to a systemic Th2 immune phenotype in pancreatic carcinoma patients
- PMID: 10433946
- PMCID: PMC1866873
- DOI: 10.1016/s0002-9440(10)65149-8
Tumor-associated transforming growth factor-beta and interleukin-10 contribute to a systemic Th2 immune phenotype in pancreatic carcinoma patients
Abstract
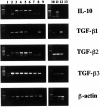
In this study, we report coexpression of transforming growth factor-beta (TGF-beta) and interleukin-10 (IL-10) in pancreatic carcinoma tissue associated with significantly elevated levels of both cytokines in the sera of pancreatic carcinoma patients. Using conditioned media (CM) of pancreatic carcinoma cells, we further demonstrate that tumor cell-derived TGF-beta and IL-10 inhibited in an additive fashion both proliferation and the development of Th1-like responses in peripheral blood mononuclear cell (PBMC) preparations derived from normal donors. The antiproliferative and Th1-suppressive activities contained in CM of pancreatic carcinoma cells were due primarily to IL-10 and/or TGF-beta, as shown by the capacity of cytokine-specific neutralizing antibodies to reverse these effects. Finally, as compared to normal controls, PBMC derived from pancreatic carcinoma patients displayed a Th2-like cytokine expression pattern upon activation with either anti-CD3 antibody or Staphylococcus aureus strain Cowan I. Taken together, these results suggest that aberrant production of TGF-beta and IL-10 in pancreatic tumor patients skews T-cell cytokine production patterns in favor of a Th2 immunophenotype.
Figures


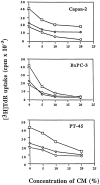

 ) shows
proliferation in the presence of BxPC3 CM; and column 3
(▨) shows proliferation
in the presence of PT45 CM. Each column shows the mean ± SD of
three independent experiments using three different normal donors.
Results are expressed as a percentage of [3H]TdR uptake
relative to that of cells grown in the absence of either neutralizing
antibodies or CM. No effect was observed in the presence of a nonimmune
rabbit antiserum used as the control (data not
shown). Asterisks indicate statistically
significant differences (P < 0.05 in Student’s
t-tests) of data sets when compared
to controls in the presence of anti-IL-10 and anti-TGF-β neutralizing
antibodies.
) shows
proliferation in the presence of BxPC3 CM; and column 3
(▨) shows proliferation
in the presence of PT45 CM. Each column shows the mean ± SD of
three independent experiments using three different normal donors.
Results are expressed as a percentage of [3H]TdR uptake
relative to that of cells grown in the absence of either neutralizing
antibodies or CM. No effect was observed in the presence of a nonimmune
rabbit antiserum used as the control (data not
shown). Asterisks indicate statistically
significant differences (P < 0.05 in Student’s
t-tests) of data sets when compared
to controls in the presence of anti-IL-10 and anti-TGF-β neutralizing
antibodies.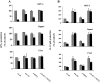
References
-
- Wolfel T, Van Pel A, Brichard V, Schneider J, Seliger B, Meyer zum Buschenfelde KH, Boon T: Two tyrosinase nonapeptides recognized on HLA-A2 melanomas by autologous cytolytic T lymphocytes. Eur J Immunol 1994, 24:759-764 - PubMed
-
- Sulitzeanu D: Immunosuppressive factors in human cancer. Adv Cancer Res 1993, 60:247-267 - PubMed
-
- Massague J: The transforming growth factor-beta family. Annu Rev Cell Biol 1990, 6:597-641 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

