Distinct actions and cooperative roles of ROCK and mDia in Rho small G protein-induced reorganization of the actin cytoskeleton in Madin-Darby canine kidney cells
- PMID: 10436006
- PMCID: PMC25478
- DOI: 10.1091/mbc.10.8.2481
Distinct actions and cooperative roles of ROCK and mDia in Rho small G protein-induced reorganization of the actin cytoskeleton in Madin-Darby canine kidney cells
Abstract
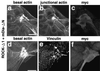
Rho, a member of the Rho small G protein family, regulates the formation of stress fibers and focal adhesions in various types of cultured cells. We investigated here the actions of ROCK and mDia, both of which have been identified to be putative downstream target molecules of Rho, in Madin-Darby canine kidney cells. The dominant active mutant of RhoA induced the formation of parallel stress fibers and focal adhesions, whereas the dominant active mutant of ROCK induced the formation of stellate stress fibers and focal adhesions, and the dominant active mutant of mDia induced the weak formation of parallel stress fibers without affecting the formation of focal adhesions. In the presence of C3 ADP-ribosyltransferase for Rho, the dominant active mutant of ROCK induced the formation of stellate stress fibers and focal adhesions, whereas the dominant active mutant of mDia induced only the diffuse localization of actin filaments. These results indicate that ROCK and mDia show distinct actions in reorganization of the actin cytoskeleton. The dominant negative mutant of either ROCK or mDia inhibited the formation of stress fibers and focal adhesions, indicating that both ROCK and mDia are necessary for the formation of stress fibers and focal adhesions. Moreover, inactivation and reactivation of both ROCK and mDia were necessary for the 12-O-tetradecanoylphorbol-13-acetate-induced disassembly and reassembly, respectively, of stress fibers and focal adhesions. The morphologies of stress fibers and focal adhesions in the cells expressing both the dominant active mutants of ROCK and mDia were not identical to those induced by the dominant active mutant of Rho. These results indicate that at least ROCK and mDia cooperatively act as downstream target molecules of Rho in the Rho-induced reorganization of the actin cytoskeleton.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Multiple downstream signalling pathways from ROCK, a target molecule of Rho small G protein, in reorganization of the actin cytoskeleton in Madin-Darby canine kidney cells.Genes Cells. 2000 Nov;5(11):929-936. doi: 10.1046/j.1365-2443.2000.00377.x. Genes Cells. 2000. PMID: 11122380
-
Rho and Rab small G proteins coordinately reorganize stress fibers and focal adhesions in MDCK cells.Mol Biol Cell. 1998 Sep;9(9):2561-75. doi: 10.1091/mbc.9.9.2561. Mol Biol Cell. 1998. PMID: 9725912 Free PMC article.
-
Involvement of an SHP-2-Rho small G protein pathway in hepatocyte growth factor/scatter factor-induced cell scattering.Mol Biol Cell. 2000 Aug;11(8):2565-75. doi: 10.1091/mbc.11.8.2565. Mol Biol Cell. 2000. PMID: 10930454 Free PMC article.
-
Rho effectors and reorganization of actin cytoskeleton.FEBS Lett. 1997 Jun 23;410(1):68-72. doi: 10.1016/s0014-5793(97)00317-7. FEBS Lett. 1997. PMID: 9247125 Review.
-
[Rho-mediated signal transduction and its physiological roles].Nihon Yakurigaku Zasshi. 2003 Mar;121(3):153-62. doi: 10.1254/fpj.121.153. Nihon Yakurigaku Zasshi. 2003. PMID: 12673949 Review. Japanese.
Cited by
-
The transcriptional activity of Sox9 in chondrocytes is regulated by RhoA signaling and actin polymerization.Mol Cell Biol. 2009 Aug;29(15):4262-73. doi: 10.1128/MCB.01779-08. Epub 2009 May 26. Mol Cell Biol. 2009. PMID: 19470758 Free PMC article.
-
A transcriptional cross-talk between RhoA and c-Myc inhibits the RhoA/Rock-dependent cytoskeleton.Oncogene. 2010 Jul 1;29(26):3781-92. doi: 10.1038/onc.2010.134. Epub 2010 May 10. Oncogene. 2010. PMID: 20453885 Free PMC article.
-
ICAM-1 nanoclusters regulate hepatic epithelial cell polarity by leukocyte adhesion-independent control of apical actomyosin.Elife. 2024 Apr 10;12:RP89261. doi: 10.7554/eLife.89261. Elife. 2024. PMID: 38597186 Free PMC article.
-
Citron kinase, a Rho-dependent kinase, induces di-phosphorylation of regulatory light chain of myosin II.Mol Biol Cell. 2003 May;14(5):1745-56. doi: 10.1091/mbc.e02-07-0427. Epub 2003 Feb 6. Mol Biol Cell. 2003. PMID: 12802051 Free PMC article.
-
A conserved mechanism for Bni1- and mDia1-induced actin assembly and dual regulation of Bni1 by Bud6 and profilin.Mol Biol Cell. 2004 Feb;15(2):896-907. doi: 10.1091/mbc.e03-08-0621. Epub 2003 Dec 2. Mol Biol Cell. 2004. PMID: 14657240 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Amano M, Chihara K, Kimura K, Fukata Y, Nakamura N, Matsuura Y, Kaibuchi K. Formation of actin stress fibers and focal adhesions enhanced by Rho-kinase. Science. 1997;275:1308–1311. - PubMed
-
- Bucci C, Parton RG, Mather IH, Stunnenberg H, Simons K, Hoflack B, Zerial M. The small GTPase rab5 functions as a regulatory factor in the early endocytic pathway. Cell. 1992;70:715–728. - PubMed
-
- Evangelista M, Blundell K, Longtine MS, Chow CJ, Adames N, Pringle JR, Peter M, Boone C. Bni1p, a yeast formin linking Cdc42p and the actin cytoskeleton during polarized morphogenesis. Science. 1997;276:118–122. - PubMed
-
- Frazier JA, Field CM. Actin cytoskeleton: are FH proteins local organizers? Curr Biol. 1997;7:R414–R417. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

