Regulation of F-actin binding to platelet moesin in vitro by both phosphorylation of threonine 558 and polyphosphatidylinositides
- PMID: 10436021
- PMCID: PMC25498
- DOI: 10.1091/mbc.10.8.2669
Regulation of F-actin binding to platelet moesin in vitro by both phosphorylation of threonine 558 and polyphosphatidylinositides
Abstract
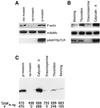
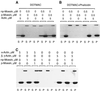
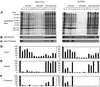
Activation of human platelets with thrombin transiently increases phosphorylation at (558)threonine of moesin as determined with phosphorylation state-specific antibodies. This specific modification is completely inhibited by the kinase inhibitor staurosporine and maximally promoted by the phosphatase inhibitor calyculin A, making it possible to purify the two forms of moesin to homogeneity. Blot overlay assays with F-actin probes labeled with either [32P]ATP or 125I show that only phosphorylated moesin interacts with F-actin in total platelet lysates, in moesin antibody immunoprecipitates, and when purified. In the absence of detergents, both forms of the isolated protein are aggregated. Phosphorylated, purified moesin co-sediments with alpha- or beta/gamma-actin filaments in cationic, but not in anionic, nonionic, or amphoteric detergents. The interaction affinity is high (Kd, approximately 1.5 nM), and the maximal moesin:actin stoichiometry is 1:1. This interaction is also observed in platelets extracted with cationic but not with nonionic detergents. In 0.1% Triton X-100, F-actin interacts with phosphorylated moesin only in the presence of polyphosphatidylinositides. Thus, both polyphosphatidylinositides and phosphorylation can activate moesin's high-affinity F-actin binding site in vitro. Dual regulation by both mechanisms may be important for proper cellular control of moesin-mediated linkages between the actin cytoskeleton and the plasma membrane.
Figures






Similar articles
-
Phosphorylation of threonine 558 in the carboxyl-terminal actin-binding domain of moesin by thrombin activation of human platelets.J Biol Chem. 1995 Dec 29;270(52):31377-85. doi: 10.1074/jbc.270.52.31377. J Biol Chem. 1995. PMID: 8537411
-
Protein phosphatase 2C inactivates F-actin binding of human platelet moesin.J Biol Chem. 1999 Sep 17;274(38):26705-12. doi: 10.1074/jbc.274.38.26705. J Biol Chem. 1999. PMID: 10480873
-
Replacement of threonine 558, a critical site of phosphorylation of moesin in vivo, with aspartate activates F-actin binding of moesin. Regulation by conformational change.J Biol Chem. 1999 Apr 30;274(18):12803-10. doi: 10.1074/jbc.274.18.12803. J Biol Chem. 1999. PMID: 10212266
-
Potential Role of Moesin in Regulating Mast Cell Secretion.Int J Mol Sci. 2023 Jul 28;24(15):12081. doi: 10.3390/ijms241512081. Int J Mol Sci. 2023. PMID: 37569454 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Actin-binding proteins.Curr Opin Cell Biol. 1990 Feb;2(1):41-50. doi: 10.1016/s0955-0674(05)80029-8. Curr Opin Cell Biol. 1990. PMID: 2158333 Review. No abstract available.
Cited by
-
G protein-coupled receptor kinase 2-mediated phosphorylation of ezrin is required for G protein-coupled receptor-dependent reorganization of the actin cytoskeleton.Mol Biol Cell. 2005 Jul;16(7):3088-99. doi: 10.1091/mbc.e04-10-0877. Epub 2005 Apr 20. Mol Biol Cell. 2005. PMID: 15843435 Free PMC article.
-
ERM-1 Phosphorylation and NRFL-1 Redundantly Control Lumen Formation in the C. elegans Intestine.Front Cell Dev Biol. 2022 Feb 7;10:769862. doi: 10.3389/fcell.2022.769862. eCollection 2022. Front Cell Dev Biol. 2022. PMID: 35198555 Free PMC article.
-
Activation of F-actin binding capacity of ezrin: synergism of PIP₂ interaction and phosphorylation.Biophys J. 2011 Apr 6;100(7):1708-17. doi: 10.1016/j.bpj.2011.02.039. Biophys J. 2011. PMID: 21463584 Free PMC article.
-
Leading from the Back: The Role of the Uropod in Neutrophil Polarization and Migration.Dev Cell. 2016 Jul 25;38(2):161-9. doi: 10.1016/j.devcel.2016.06.031. Dev Cell. 2016. PMID: 27459068 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Phospholipase C-mediated hydrolysis of PIP2 releases ERM proteins from lymphocyte membrane.J Cell Biol. 2009 Feb 9;184(3):451-62. doi: 10.1083/jcb.200807047. J Cell Biol. 2009. PMID: 19204146 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Amieva MR, Furthmayr H. Subcellular localization of moesin in dynamic filopodia, retraction fibers, and other structures involved in substrate exploration, attachment, and cell-cell contacts. Exp Cell Res. 1995;219:180–196. - PubMed
-
- Amieva MR, Litman P, Huang L, Ichimaru E, Furthmayr H. Disruption of dynamic cell surface architecture of NIH3T3 fibroblasts by the N-terminal domains of moesin and ezrin: in vivo imaging with GFP fusion proteins. J Cell Sci. 1998;112:111–125. - PubMed
-
- Benka ML, et al. The thrombin receptor in human platelets is coupled to a GTP binding protein of the G alpha q family. FEBS Lett. 1995;363:49–52. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials

