Tetanus toxin blocks the exocytosis of synaptic vesicles clustered at synapses but not of synaptic vesicles in isolated axons
- PMID: 10436029
- PMCID: PMC6782867
- DOI: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.19-16-06723.1999
Tetanus toxin blocks the exocytosis of synaptic vesicles clustered at synapses but not of synaptic vesicles in isolated axons
Abstract
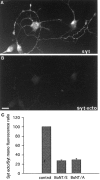
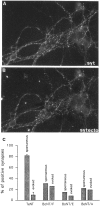
Recycling synaptic vesicles are already present in isolated axons of developing neurons (Matteoli et al., Zakharenko et al., 1999). This vesicle recycling is distinct from the vesicular traffic implicated in axon outgrowth. Formation of synaptic contacts coincides with a clustering of synaptic vesicles at the contact site and with a downregulation of their basal rate of exo-endocytosis (Kraszewski et al, 1995; Coco et al., 1998) We report here that tetanus toxin-mediated cleavage of synaptobrevin/vesicle-associated membrane protein (VAMP2), previously shown not to affect axon outgrowth, also does not inhibit synaptic vesicle exocytosis in isolated axons, despite its potent blocking effect on their exocytosis at synapses. This differential effect of tetanus toxin could be seen even on different branches of a same neuron. In contrast, botulinum toxins A and E [which cleave synaptosome-associated protein of 25 kDa. (SNAP-25)] and F (which cleaves synaptobrevin/VAMP1 and 2) blocked synaptic vesicle exocytosis both in isolated axons and at synapses, strongly suggesting that this process is dependent on "classical" synaptic SNAP receptor (SNARE) complexes both before and after synaptogenesis. A tetanus toxin-resistant form of synaptic vesicle recycling, which proceeds in the absence of external stimuli and is sensitive to botulinum toxin F, E, and A, persists at mature synapses. These data suggest the involvement of a tetanus toxin-resistant, but botulinum F-sensitive, isoform of synaptobrevin/VAMP in synaptic vesicle exocytosis before synapse formation and the partial persistence of this form of exocytosis at mature synaptic contacts.
Figures




Similar articles
-
Botulinum neurotoxin A blocks synaptic vesicle exocytosis but not endocytosis at the nerve terminal.J Cell Biol. 1999 Dec 13;147(6):1249-60. doi: 10.1083/jcb.147.6.1249. J Cell Biol. 1999. PMID: 10601338 Free PMC article.
-
Role of tetanus neurotoxin insensitive vesicle-associated membrane protein (TI-VAMP) in vesicular transport mediating neurite outgrowth.J Cell Biol. 2000 May 15;149(4):889-900. doi: 10.1083/jcb.149.4.889. J Cell Biol. 2000. PMID: 10811829 Free PMC article.
-
Ca2+-dependent regulation of synaptic SNARE complex assembly via a calmodulin- and phospholipid-binding domain of synaptobrevin.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2000 Aug 15;97(17):9695-700. doi: 10.1073/pnas.97.17.9695. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2000. PMID: 10944231 Free PMC article.
-
[Molecular biology of neurosecretion and its inhibition bu tetanus and botulinum toxins (review)].Berl Munch Tierarztl Wochenschr. 1999 Jun;112(5):186-91. Berl Munch Tierarztl Wochenschr. 1999. PMID: 10399406 Review. German.
-
[Analysis of synaptic neurotransmitter release mechanisms using bacterial toxins].J Soc Biol. 1999;193(6):457-67. J Soc Biol. 1999. PMID: 10783704 Review. French.
Cited by
-
A New Behavioral Test and Associated Genetic Tools Highlight the Function of Ventral Abdominal Muscles in Adult Drosophila.Front Cell Neurosci. 2017 Nov 21;11:371. doi: 10.3389/fncel.2017.00371. eCollection 2017. Front Cell Neurosci. 2017. PMID: 29209177 Free PMC article.
-
The orphan receptor GPR17 identified as a new dual uracil nucleotides/cysteinyl-leukotrienes receptor.EMBO J. 2006 Oct 4;25(19):4615-27. doi: 10.1038/sj.emboj.7601341. Epub 2006 Sep 21. EMBO J. 2006. PMID: 16990797 Free PMC article.
-
Transsynaptic N-Cadherin Adhesion Complexes Control Presynaptic Vesicle and Bulk Endocytosis at Physiological Temperature.Front Cell Neurosci. 2021 Oct 7;15:713693. doi: 10.3389/fncel.2021.713693. eCollection 2021. Front Cell Neurosci. 2021. PMID: 34759800 Free PMC article.
-
Semimechanistic Population Pharmacokinetic Modeling to Investigate Amyloid Beta Trafficking and Accumulation at the BBB Endothelium.Mol Pharm. 2021 Nov 1;18(11):4148-4161. doi: 10.1021/acs.molpharmaceut.1c00549. Epub 2021 Oct 19. Mol Pharm. 2021. PMID: 34664956 Free PMC article.
-
Synaptic vesicle protein trafficking at the glutamate synapse.Neuroscience. 2009 Jan 12;158(1):189-203. doi: 10.1016/j.neuroscience.2008.03.029. Epub 2008 Mar 22. Neuroscience. 2009. PMID: 18472224 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Ahnert-Hilger G, Kutay U, Chahoud I, Rapoport T, Wiedenmann B. Synaptobrevin is essential for secretion but not for the development of synaptic processes. Eur J Cell Biol. 1996;70:1–11. - PubMed
-
- Banker GA, Cowan WM. Rat hippocampal neurons in dispersed cell culture. Brain Res. 1977;126:379–425. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
