Embryonic lethal abnormal vision-like RNA-binding proteins regulate neurite outgrowth and tau expression in PC12 cells
- PMID: 10436048
- PMCID: PMC6782881
- DOI: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.19-16-06907.1999
Embryonic lethal abnormal vision-like RNA-binding proteins regulate neurite outgrowth and tau expression in PC12 cells
Abstract
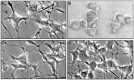
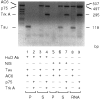
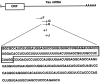
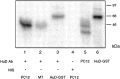
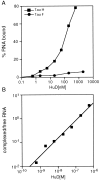
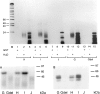
The embryonic lethal abnormal vision (ELAV)-like proteins are mRNA-binding proteins that regulate mRNA stability. The neuronal members of this family are required for neuronal differentiation. We identified the binding region of purified HuD protein to a target neuronal mRNA encoding for the tau microtubule-associated protein and demonstrated an in vivo interaction between the ELAV-like protein and its target tau mRNA. We show that treatment of neuronal cells with antisense oligodeoxynucleotides directed against HuD blocks the induction of neurite outgrowth and decreases the levels of tau mRNAs, indicating that the ELAV-like proteins are required for neuronal differentiation.
Figures




Similar articles
-
The RNA-binding protein HuD is required for GAP-43 mRNA stability, GAP-43 gene expression, and PKC-dependent neurite outgrowth in PC12 cells.Mol Biol Cell. 2000 Sep;11(9):3191-203. doi: 10.1091/mbc.11.9.3191. Mol Biol Cell. 2000. PMID: 10982410 Free PMC article.
-
Cytoplasmic localization is required for the mammalian ELAV-like protein HuD to induce neuronal differentiation.Genes Cells. 1999 Nov;4(11):667-83. doi: 10.1046/j.1365-2443.1999.00292.x. Genes Cells. 1999. PMID: 10620013
-
Overexpression of HuD, but not of its truncated form HuD I+II, promotes GAP-43 gene expression and neurite outgrowth in PC12 cells in the absence of nerve growth factor.J Neurochem. 2000 Sep;75(3):1103-14. doi: 10.1046/j.1471-4159.2000.0751103.x. J Neurochem. 2000. PMID: 10936192
-
Role of HuD and other RNA-binding proteins in neural development and plasticity.J Neurosci Res. 2002 Apr 15;68(2):121-6. doi: 10.1002/jnr.10175. J Neurosci Res. 2002. PMID: 11948657 Review.
-
Emerging complexity of the HuD/ELAVl4 gene; implications for neuronal development, function, and dysfunction.RNA. 2013 Aug;19(8):1019-37. doi: 10.1261/rna.039164.113. RNA. 2013. PMID: 23861535 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Neuron-specific ELAV/Hu proteins suppress HuR mRNA during neuronal differentiation by alternative polyadenylation.Nucleic Acids Res. 2012 Mar;40(6):2734-46. doi: 10.1093/nar/gkr1114. Epub 2011 Dec 1. Nucleic Acids Res. 2012. PMID: 22139917 Free PMC article.
-
The RNA-binding protein HuD is required for GAP-43 mRNA stability, GAP-43 gene expression, and PKC-dependent neurite outgrowth in PC12 cells.Mol Biol Cell. 2000 Sep;11(9):3191-203. doi: 10.1091/mbc.11.9.3191. Mol Biol Cell. 2000. PMID: 10982410 Free PMC article.
-
Association between the neuron-specific RNA-binding protein ELAVL4 and Parkinson disease.Hum Genet. 2005 Jun;117(1):27-33. doi: 10.1007/s00439-005-1259-2. Epub 2005 Apr 13. Hum Genet. 2005. PMID: 15827745
-
MRNA stability and the control of gene expression: implications for human disease.Neurochem Res. 2002 Oct;27(10):957-80. doi: 10.1023/a:1020992418511. Neurochem Res. 2002. PMID: 12462398 Review.
-
Post-transcriptional regulatory elements and spatiotemporal specification of neocortical stem cells and projection neurons.Neuroscience. 2013 Sep 17;248:499-528. doi: 10.1016/j.neuroscience.2013.05.042. Epub 2013 May 30. Neuroscience. 2013. PMID: 23727006 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Aronov S, Marx R, Ginzburg I (1999) Identification of 3′ UTR sequences implicated in tau mRNA stabilization. J Mol Neurosci, in press. - PubMed
-
- Abe R, Uyeno Y, Yamamoto K, Sakamoto H. Tissue-specific expression of the gene encoding a mouse RNA binding protein homologous to human HuD antigen. DNA Res. 1994;1:175–180. - PubMed
-
- Antic D, Keene JD. Messenger ribonucleoprotein complexes containing human ELAV proteins: interactions with cytoskeleton and translational apparatus. J Cell Sci. 1998;111:183–197. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
