Long-term enhancement of central synaptic transmission by chronic brain-derived neurotrophic factor treatment
- PMID: 10436057
- PMCID: PMC6782869
- DOI: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.19-16-07025.1999
Long-term enhancement of central synaptic transmission by chronic brain-derived neurotrophic factor treatment
Abstract
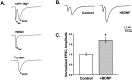
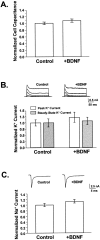
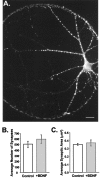
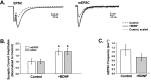
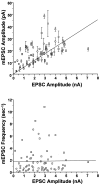
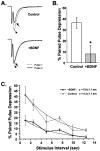
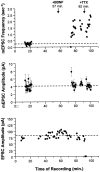
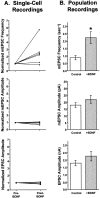
Acute effects of neurotrophins on synaptic plasticity have recently received much attention, but the roles of these factors in regulating long-lasting changes in synaptic function remain unclear. To address this issue we studied the long-term (days to weeks) and short-term (minutes to hours) effects of brain-derived neurotrophic factor (BDNF) on excitatory synaptic transmission in autaptic cultures of hippocampal CA1 neurons. We found that BDNF induced long-term enhancement of the strength of non-NMDA receptor-mediated glutamatergic transmission. This upregulation of EPSC amplitude occurred via an increase in the size of unitary synaptic currents, with no significant contribution from other aspects of neuronal electrical and synaptic function including cell size, voltage-gated sodium and potassium current levels, the number and size of synaptic contacts, and the frequency of spontaneous neurotransmitter release. Chronic BDNF treatment also decreased the degree of synaptic depression measured in response to paired stimuli. Thus, BDNF induced long-term synaptic enhancement of both basal and use-dependent synaptic transmission via specific changes to the synapse rather than through generalized potentiation of neuronal growth and differentiation. Finally, we showed that the long-term effects of BDNF are functionally and mechanistically distinct from its acute effects on synaptic transmission, suggesting that, in vivo, BDNF activation of Trk receptors can have different functional effects depending on the time course of its action.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Modulation of unitary glutamatergic synapses by neurotrophin-4/5 or brain-derived neurotrophic factor in hippocampal microcultures: presynaptic enhancement depends on pre-established paired-pulse facilitation.Neuroscience. 1998 Sep;86(2):399-413. doi: 10.1016/s0306-4522(98)00035-9. Neuroscience. 1998. PMID: 9881855
-
Enhancement of neurotransmitter release induced by brain-derived neurotrophic factor in cultured hippocampal neurons.J Neurosci. 1998 Dec 15;18(24):10231-40. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.18-24-10231.1998. J Neurosci. 1998. PMID: 9852560 Free PMC article.
-
Presynaptic and postsynaptic NMDA receptors mediate distinct effects of brain-derived neurotrophic factor on synaptic transmission.J Neurophysiol. 2008 Dec;100(6):3175-84. doi: 10.1152/jn.90880.2008. Epub 2008 Oct 15. J Neurophysiol. 2008. PMID: 18922945 Free PMC article.
-
Neurotrophin-dependent modulation of glutamatergic synaptic transmission in the mammalian CNS.Gen Pharmacol. 1998 Nov;31(5):667-74. doi: 10.1016/s0306-3623(98)00190-6. Gen Pharmacol. 1998. PMID: 9809461 Review.
-
Long-term regulation of excitatory and inhibitory synaptic transmission in hippocampal cultures by brain-derived neurotrophic factor.Prog Brain Res. 2000;128:203-18. doi: 10.1016/s0079-6123(00)28018-7. Prog Brain Res. 2000. PMID: 11105680 Review. No abstract available.
Cited by
-
BDNF and activity-dependent synaptic modulation.Learn Mem. 2003 Mar-Apr;10(2):86-98. doi: 10.1101/lm.54603. Learn Mem. 2003. PMID: 12663747 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Effects of neurotrophins on cortical plasticity: same or different?J Neurosci. 2000 Mar 15;20(6):2155-65. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.20-06-02155.2000. J Neurosci. 2000. PMID: 10704490 Free PMC article.
-
Docosahexaenoic acid dietary supplementation enhances the effects of exercise on synaptic plasticity and cognition.Neuroscience. 2008 Aug 26;155(3):751-9. doi: 10.1016/j.neuroscience.2008.05.061. Epub 2008 Jun 17. Neuroscience. 2008. PMID: 18620024 Free PMC article.
-
Transforming growth factor alpha attenuates the functional expression of AMPA receptors in cortical GABAergic neurons.Mol Cell Neurosci. 2006 Apr;31(4):628-41. doi: 10.1016/j.mcn.2005.12.002. Epub 2006 Jan 26. Mol Cell Neurosci. 2006. PMID: 16443372 Free PMC article.
-
Altered balance of glutamatergic/GABAergic synaptic input and associated changes in dendrite morphology after BDNF expression in BDNF-deficient hippocampal neurons.J Neurosci. 2006 Jul 5;26(27):7189-200. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.5474-05.2006. J Neurosci. 2006. PMID: 16822976 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous
