Truncated apolipoprotein E (ApoE) causes increased intracellular calcium and may mediate ApoE neurotoxicity
- PMID: 10436064
- PMCID: PMC6782866
- DOI: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.19-16-07100.1999
Truncated apolipoprotein E (ApoE) causes increased intracellular calcium and may mediate ApoE neurotoxicity
Abstract
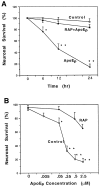
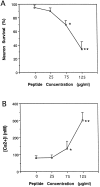
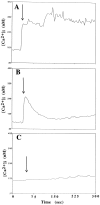
Apolipoprotein E (apoE)-related synthetic peptides, the 22 kDa N-terminal thrombin-cleavage fragment of apoE (truncated apoE), and full-length apoE have all been shown to exhibit neurotoxic activity under certain culture conditions. In the present study, protease inhibitors reduced the neurotoxicity and proteolysis of full-length apoE but did not block the toxicity of truncated apoE or a synthetic apoE peptide, suggesting that fragments of apoE may account for its toxicity. Additional experiments demonstrated that both truncated apoE and the apoE peptide elicit an increase in intracellular calcium levels and subsequent death of embryonic rat hippocampal neurons in culture. Similar effects on calcium were found when the apoE peptide was applied to chick sympathetic neurons. The rise in intracellular calcium and the hippocampal cell death caused by the apoE peptide were significantly reduced by receptor-associated protein, removal of extracellular calcium, or administration of the specific NMDA glutamate receptor antagonist MK-801. These results suggest that apoE may be a source of both neurotoxicity and calcium influx that involves cell surface receptors. Such findings strengthen the hypothesis that apoE plays a direct role in the pathology of Alzheimer's disease.
Figures






Similar articles
-
Multiple pathways of apolipoprotein E signaling in primary neurons.J Neurochem. 2005 Apr;93(1):145-55. doi: 10.1111/j.1471-4159.2004.03007.x. J Neurochem. 2005. PMID: 15773914
-
Neurotoxicity of the 22 kDa thrombin-cleavage fragment of apolipoprotein E and related synthetic peptides is receptor-mediated.J Neurosci. 1997 Aug 1;17(15):5678-86. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.17-15-05678.1997. J Neurosci. 1997. PMID: 9221767 Free PMC article.
-
Injury-induced synthesis and release of apolipoprotein E and clusterin from rat neural cells.Eur J Neurosci. 1996 Dec;8(12):2652-61. doi: 10.1111/j.1460-9568.1996.tb01560.x. Eur J Neurosci. 1996. PMID: 8996815
-
Lowering extracellular Na+ concentration causes NMDA receptor-mediated neuronal death in cultured rat hippocampal slices.Brain Res. 1996 Sep 30;735(1):1-8. doi: 10.1016/s0006-8993(96)00536-7. Brain Res. 1996. PMID: 8905163
-
Rapid elevation of neuronal cytoplasmic calcium by apolipoprotein E peptide.J Cell Physiol. 1997 Oct;173(1):73-83. doi: 10.1002/(SICI)1097-4652(199710)173:1<73::AID-JCP9>3.0.CO;2-G. J Cell Physiol. 1997. PMID: 9326451
Cited by
-
Neuron-specific apolipoprotein e4 proteolysis is associated with increased tau phosphorylation in brains of transgenic mice.J Neurosci. 2004 Mar 10;24(10):2527-34. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.4315-03.2004. J Neurosci. 2004. PMID: 15014128 Free PMC article.
-
Apolipoprotein E4: a causative factor and therapeutic target in neuropathology, including Alzheimer's disease.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2006 Apr 11;103(15):5644-51. doi: 10.1073/pnas.0600549103. Epub 2006 Mar 27. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2006. PMID: 16567625 Free PMC article. Review.
-
A dual role for apolipoprotein e in neuroinflammation: anti- and pro-inflammatory activity.J Mol Neurosci. 2004;23(3):205-12. doi: 10.1385/JMN:23:3:205. J Mol Neurosci. 2004. PMID: 15181248
-
Carboxyl-terminal-truncated apolipoprotein E4 causes Alzheimer's disease-like neurodegeneration and behavioral deficits in transgenic mice.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2003 Sep 16;100(19):10966-71. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1434398100. Epub 2003 Aug 25. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2003. PMID: 12939405 Free PMC article.
-
Neuronal apoptosis by apolipoprotein E4 through low-density lipoprotein receptor-related protein and heterotrimeric GTPases.J Neurosci. 2000 Nov 15;20(22):8401-9. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.20-22-08401.2000. J Neurosci. 2000. PMID: 11069947 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Ankarcrona M, Dypbukt JM, Bonfoco E, Zhivotovsky B, Orrenius S, Lipton SA, Nicotera P. Glutamate-induced neuronal death: a succession of necrosis or apoptosis depending on mitochondrial function. Neuron. 1995;15:961–973. - PubMed
-
- Beisiegel U, Weber W, Ihrke G, Herz J, Stanley KK. The LDL-receptor-related protein, LRP, is an apolipoprotein E-binding protein. Nature. 1989;341:162–164. - PubMed
-
- Bellosta S, Nathan BP, Orth M, Dong L-M, Mahley RW, Pitas RE. Stable expression and secretion of apolipoproteins E3 and E4 in mouse neuroblastoma cells produces differential effects on neurite outgrowth. J Biol Chem. 1995;270:27063–27071. - PubMed
-
- Blacker D, Wilcox M, Laird N, Rodes L, Horvath SM, Go RCP, Perry R, Watson B, Jr, Bassett SS, McInnis MG, Albert MS, Hyman BT, Tanzi RE. Alpha-2 macroglobulin is genetically associated with Alzheimer disease. Nat Genet. 1998;19:357–360. - PubMed
-
- Cavallaro U, Nykjaer A, Nielsen M, Soria MR. Alpha 2-macroglobulin receptor mediates binding and cytotoxicity of plant ribosome-inactivating proteins. Eur J Biochem. 1995;232:165–171. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous
