Staphylococcus aureus cap5P encodes a UDP-N-acetylglucosamine 2-epimerase with functional redundancy
- PMID: 10438750
- PMCID: PMC93967
- DOI: 10.1128/JB.181.16.4818-4824.1999
Staphylococcus aureus cap5P encodes a UDP-N-acetylglucosamine 2-epimerase with functional redundancy
Abstract
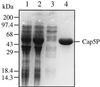
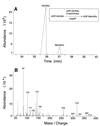
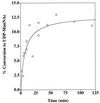
The serotype 5 capsule gene cluster of Staphylococcus aureus comprises 16 genes (cap5A through cap5P), but little is known about how the putative gene products function in capsule biosynthesis. We propose that the N-acetylmannosaminuronic acid (ManNAcA) component of the S. aureus serotype 5 capsular polysaccharide (CP5) is synthesized from a UDP-N-acetylglucosamine (UDP-GlcNAc) precursor that is epimerized to UDP-N-acetylmannosamine (UDP-ManNAc) and then oxidized to UDP-ManNAcA. We report the purification and biochemical characterization of a recombinant UDP-GlcNAc 2-epimerase encoded by S. aureus cap5P. Purified Cap5P converted approximately 10% of UDP-GlcNAc to UDP-ManNAc as detected by gas chromatography-mass spectrometry. The epimerization of UDP-GlcNAc to UDP-ManNAc occurred over a wide pH range and was unaffected by divalent cations. Surprisingly, CP5 expression in S. aureus was unaffected by insertional inactivation of cap5P. Sequence homology searches of the public S. aureus genomic databases revealed the presence of another putative UDP-GlcNAc 2-epimerase on the S. aureus chromosome that showed 61% identity to Cap5P. Redundancy of UDP-GlcNAc 2-epimerase function in S. aureus was demonstrated by cloning the cap5P homologue from strain Newman and complementing an Escherichia coli rffE mutant defective in UDP-GlcNAc 2-epimerase activity. Our results confirm the putative function of the S. aureus cap5P gene product and demonstrate the presence of a second gene on the staphylococcal chromosome with a similar function.
Figures

References
-
- Bhasin N, Albus A, Michon F, Livolsi P J, Park J-S, Lee J C. Identification of a gene essential for O-acetylation of the Staphylococcus aureus type 5 capsular polysaccharide. Mol Microbiol. 1998;27:9–21. - PubMed
-
- Bradford M. A rapid and sensitive method for the quantitation of microgram quantities of protein utilizing the principle of protein-dye binding. Anal Biochem. 1976;72:248–254. - PubMed
-
- Edman P. Method for determination of the amino acid sequence in peptides. Acta Chem Scand. 1950;4:283–293.
-
- Institute of Genomic Research Website. 1999, copyright date. 7 April 1999, revision date. Sequences. [Online.] The Institute for Genomic Research. http://www.tigr.org. [5 July 1999, last date accessed.]
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
- Actions
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

