InvF is required for expression of genes encoding proteins secreted by the SPI1 type III secretion apparatus in Salmonella typhimurium
- PMID: 10438766
- PMCID: PMC93983
- DOI: 10.1128/JB.181.16.4949-4954.1999
InvF is required for expression of genes encoding proteins secreted by the SPI1 type III secretion apparatus in Salmonella typhimurium
Abstract
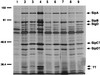
The expression of genes encoding proteins secreted by the SPI1 (Salmonella pathogenicity island) type III secretion apparatus is known to require the transcriptional activators SirA and HilA. However, neither SirA nor HilA is believed to directly activate the promoters of these genes. invF, the first gene of the inv-spa gene cluster, is predicted to encode an AraC-type transcriptional activator and is required for invasion into cultured epithelial cells. However, the genes which are regulated by InvF have not been identified. In this work, an in-frame deletion in invF was constructed and tested for the expression of Phi(sigD-lacZYA), sipC::Tn5lacZY, and a plasmid-encoded Phi(sicA-lacZYA). SigD (Salmonella invasion gene) is a secreted protein required for the efficient invasion of Salmonella typhimurium into cultured eucaryotic cells. sicA (Salmonella invasion chaperone) is the first gene of a putative operon encoding the Sip/Ssp (Salmonella invasion/Salmonella secreted proteins) invasion proteins secreted by the SPI1 type III export apparatus. invF was required for the expression of the sigD, sicA, and sipC fusions. This is the first demonstration that there is a functional promoter in the intergenic sequence between spaS and sicA. In addition, several proteins were either absent from or found in reduced amounts in the culture supernatants of the invF mutant. Therefore, invF is required for the optimal expression of several genes encoding SPI1-secreted proteins. Genetic evidence is also presented suggesting there is HilA-dependent readthrough transcription from the invF promoter at least through sipC.
Figures
References
-
- Ahmer B M M, van Reeuwijk J, Watson P R, Wallis T S, Heffron F. Salmonella SirA is a global regulator of genes mediating enteropathogenesis. Mol Microbiol. 1999;31:971–982. - PubMed
-
- Altmeyer R M, McNern J K, Bossio J C, Rosenshine I, Finlay B B, Galán J E. Cloning and molecular characterization of a gene involved in Salmonella adherence and invasion of cultured epithelial cells. Mol Microbiol. 1993;7:89–98. - PubMed
-
- Bajaj V, Hwang C, Lee C A. hilA is a novel ompR/toxR family member that activates the expression of Salmonella typhimurium invasion genes. Mol Microbiol. 1995;18:715–727. - PubMed
-
- Bajaj V, Lucas R L, Hwang C, Lee C A. Co-ordinate regulation of Salmonella typhimurium invasion genes by environmental and regulatory factors is mediated by control of hilA expression. Mol Microbiol. 1996;22:703–714. - PubMed
-
- Baumler A J, Tsolis R M, van der Velden A W M, Stojiljkovik I, Anic A, Heffron F. Identification of a new iron regulated locus of Salmonella typhi. Gene. 1996;183:207–213. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

