Improving high-resolution MR bold venographic imaging using a T1 reducing contrast agent
- PMID: 10441013
- PMCID: PMC4102700
- DOI: 10.1002/(sici)1522-2586(199908)10:2<118::aid-jmri2>3.0.co;2-v
Improving high-resolution MR bold venographic imaging using a T1 reducing contrast agent
Abstract
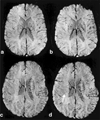
Recently, a new imaging method was proposed by Reichenbach et al (Radiology 1997;204:272-277) to image small cerebral venous vessels specifically. This method, referred to as high-resolution blood oxygen level-dependent venography (HRBV), relies on the susceptibility difference between the veins and the brain parenchyma. The resulting phase difference between the vessels and the brain parenchyma leads to signal losses over and above the usual T2* effect. At 1.5 T, a rather long TE (roughly 40 msec) is required for this cancellation to become significant, leading to enhanced susceptibility artifacts and a long data acquisition time. In this study, we examine the utility of incorporating a clinically available T1 reducing contrast agent, Omniscan (Sanofi Winthrop Pharmaceuticals, NY, NY), with the HRBV imaging approach to reduce susceptibility artifacts and imaging time while maintaining the visibility of cerebral veins. Using a double-dose injection of Omniscan, we were able to reduce TE from 40 to 25 msec. This led to a decrease in TR from 57 to 42 msec, allowing a 26% reduction in data acquisition time while maintaining the visibility of cerebral venous vessels and reducing susceptibility artifacts. J. Magn. Reson. Imaging 1999;10:118-123, 1999.
Copyright 1999 Wiley-Liss, Inc.
Figures


References
-
- Reichenbach JR, Venkatesan R, Schillinger DJ, Kido DK, Haacke EM. Small vessels in the human brain: MR venography with deoxyhemoglobin as an intrinsic contrast agent. Radiology. 1997;204:272–277. - PubMed
-
- Shaibani A, Yoon M, Haacke EM, Lin W, Lee BCP. Evaluation of angiographically occult vascular malformation using a new high-resolution technique for MR venography; Proceedings of the 36th Annual Meeting of the American Society of Neuroradiology; 1998.
-
- Haacke EM, Lai S, Reichenbach JR, et al. In vivo measurement of blood oxygen saturation using magnetic resonance imaging: a direct validation of the blood oxygen level-dependent concept in functional brain imaging. Hum Brain Mapping. 1997;5:341–346. - PubMed
-
- Yablonskiy DA, Haacke EM. Theory and NMR signal behavior in magnetically inhomogeneous tissues: the static dephasing regime. Magn Reson Med. 1994;32:749–763. - PubMed
-
- Kennan RP, Gao JH, Zhong J, Gore JC. A General model of microcirculatory blood flow effects in gradient sensitized MRI. Med Phys. 1994;21:539–545. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

