Genetic modification of hearing in tubby mice: evidence for the existence of a major gene (moth1) which protects tubby mice from hearing loss
- PMID: 10441341
- PMCID: PMC3249642
- DOI: 10.1093/hmg/8.9.1761
Genetic modification of hearing in tubby mice: evidence for the existence of a major gene (moth1) which protects tubby mice from hearing loss
Abstract
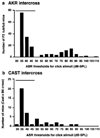
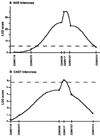
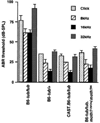
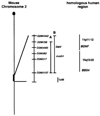
Quantitative trait locus (QTL) analysis of genetic crosses has proven to be a useful tool for identifying loci associated with specific phenotypes and for dissecting genetic components of complex traits. Inclusion of a mutation that interacts epistatically with QTLs in genetic crosses is a unique and potentially powerful method of revealing the function of novel genes and pathways. Although we know that a mutation within the novel tub gene leads to obesity and cochlear and retinal degeneration, the biological function of the gene and the mechanism by which it induces its phenotypes are not known. In the current study, a QTL analysis for auditory brainstem response (ABR) thresholds, which indicates hearing ability, was performed in tubby mice from F(2)intercrosses between C57BL/6J- tub / tub and AKR/J-+/+ F(1)hybrids (AKR intercross) and between C57BL/6J- tub / tub and CAST/Ei.B6- tub / tub F(1)hybrids (CAST intercross). A major QTL, designated asmodifieroftubbyhearing1 ( moth1 ), was identified on chromosome 2 with a LOD score of 33.4 ( P < 10(-33)) in the AKR intercross (181 mice) and of 6.0 ( P < 10(-6)) in the CAST intercross (46 mice). This QTL is responsible for 57 and 43% of ABR threshold variance, respectively, in each strain combination. In addition, a C57BL/6J congenic line carrying a 129/Ola segment encompassing the described QTL region when made homozygous for tubby also exhibits normal hearing ability. We hypothesize that C57BL/6J carries a recessive mutation of the moth1 gene which interacts with the tub mutation to cause hearing loss in tub / tub mice. A moth1 allele from either AKR/J, CAST/Ei or 129/Ola is sufficient to protect C57BL/6J- tub / tub mice from hearing loss.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Microtubule-associated protein 1A is a modifier of tubby hearing (moth1).Nat Genet. 2002 Apr;30(4):401-5. doi: 10.1038/ng838. Epub 2002 Feb 4. Nat Genet. 2002. PMID: 11925566 Free PMC article.
-
Genetic modification of retinal degeneration in tubby mice.Exp Eye Res. 2002 Apr;74(4):455-61. doi: 10.1006/exer.2001.1139. Exp Eye Res. 2002. PMID: 12076089
-
Sensitivity to dietary obesity linked to a locus on chromosome 15 in a CAST/Ei x C57BL/6J F2 intercross.Mamm Genome. 1996 Sep;7(9):677-81. doi: 10.1007/s003359900204. Mamm Genome. 1996. PMID: 8703121
-
Quantitative genetics of age-related retinal degeneration: a second F1 intercross between the A/J and C57BL/6 strains.Mol Vis. 2007 Jan 25;13:79-85. Mol Vis. 2007. PMID: 17277741 Free PMC article.
-
Strain background effects and genetic modifiers of hearing in mice.Brain Res. 2006 May 26;1091(1):79-88. doi: 10.1016/j.brainres.2006.02.021. Epub 2006 Mar 31. Brain Res. 2006. PMID: 16579977 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Molecular mechanisms underlying cochlear degeneration in the tubby mouse and the therapeutic effect of sulforaphane.Neurochem Int. 2009 Mar-Apr;54(3-4):172-9. doi: 10.1016/j.neuint.2008.08.013. Epub 2008 Dec 9. Neurochem Int. 2009. PMID: 19114066 Free PMC article.
-
At the speed of sound: gene discovery in the auditory system.Am J Hum Genet. 2001 Nov;69(5):923-35. doi: 10.1086/324122. Epub 2001 Sep 27. Am J Hum Genet. 2001. PMID: 11577373 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Microtubule-associated protein 1A is a modifier of tubby hearing (moth1).Nat Genet. 2002 Apr;30(4):401-5. doi: 10.1038/ng838. Epub 2002 Feb 4. Nat Genet. 2002. PMID: 11925566 Free PMC article.
-
Mutation screen of the TUB gene in patients with retinitis pigmentosa and Leber congenital amaurosis.Exp Eye Res. 2006 Sep;83(3):569-73. doi: 10.1016/j.exer.2006.02.003. Epub 2006 Apr 27. Exp Eye Res. 2006. PMID: 16643894 Free PMC article.
-
A QTL on Chr 5 modifies hearing loss associated with the fascin-2 variant of DBA/2J mice.Mamm Genome. 2015 Aug;26(7-8):338-47. doi: 10.1007/s00335-015-9574-y. Epub 2015 Jun 20. Mamm Genome. 2015. PMID: 26092689 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Ohlemiller KK, Hughes RM, Lett JM, Ogilvie JM, Speck JD, Wright JS, Faddis BT. Progression of cochlear and retinal degeneration in the tubby (rd5) mouse. Audiol. Neuro-Otol. 1997;2:175–185. - PubMed
-
- Ikeda S, He W, Ikeda A, Naggert JK, North MA, Nishina PM. Cell specific expression of tubby gene family members in the retina. Invest. Ophthalmol. Vis. Sci. 1999 in press. - PubMed
-
- Noben-Trauth K, Naggert JK, North MA, Nishina PM. A candidate gene for the mouse mutation tubby. Nature. 1996;380:534–538. - PubMed
-
- Kleyn PW, Fan W, Kovats SG, Lee JJ, Pulido JC, Wu Y, Berkemeier LR, Misumi DJ, Holmgren L, Charlat O, Woolf EA, Tayber O, Brody T, Shu P, Hawkins F, Kennedy B, Baldini L, Ebeling C, Alperin GD, Deeds J, Lakey ND, Culpepper J, Chen H, Glücksmann-Kuis MA, Carlson GA, Duyk GM, Moore KJ. Identification and characterization of the mouse obesity gene tubby: a member of a novel gene family. Cell. 1996;85:281–290. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

