Serum concentrations and peripheral secretion of the beta chemokines monocyte chemoattractant protein 1 and macrophage inflammatory protein 1alpha in alcoholic liver disease
- PMID: 10446112
- PMCID: PMC1727646
- DOI: 10.1136/gut.45.3.416
Serum concentrations and peripheral secretion of the beta chemokines monocyte chemoattractant protein 1 and macrophage inflammatory protein 1alpha in alcoholic liver disease
Abstract
Background: Alcoholic liver disease is associated with increased hepatic expression of monocyte chemoattractant protein 1 (MCP-1) and macrophage inflammatory protein 1alpha (MIP-1alpha).
Aims: To determine whether concentrations of chemokines in the peripheral circulation reflect disease activity, and whether chemokine secretion is restricted to the liver or is part of a systemic inflammatory response in alcoholic liver disease.
Patients: Fifty one patients with alcoholic liver disease and 12 healthy controls.
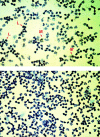
Methods: Peripheral vein (and hepatic vein in patients undergoing transjugular liver biopsy) chemokine concentrations were measured by ELISA. Chemokine secretion and transcription in isolated peripheral mononuclear cells were assessed using ELISA and in situ hybridisation in patients with severe alcoholic hepatitis.
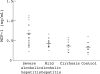
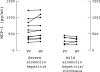
Results: Serum MCP-1 concentrations were higher in alcoholic hepatitis compared with cirrhosis or healthy controls. MIP-1alpha concentrations were below the assay sensitivity in most patients. Serum MCP-1 concentrations correlated significantly with serum aspartate aminotransferase and creatinine. In severe alcoholic hepatitis, MCP-1 concentrations were higher in hepatic compared with peripheral veins; in mild alcoholic hepatitis there was no difference. Mononuclear cell secretion of both MCP-1 and MIP-1alpha was higher in severe alcoholic hepatitis compared with healthy controls, and chemokine mRNA was identified in monocytes.
Conclusions: Serum MCP-1 concentrations are raised in alcoholic liver disease and reflect severity of hepatic inflammation. Monocyte secretion of both MCP-1 and MIP-1alpha is increased in severe alcoholic hepatitis. Both intrahepatic sources and peripheral mononuclear cells contribute to the raised serum MCP-1 concentrations.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Distinct patterns of chemokine expression are associated with leukocyte recruitment in alcoholic hepatitis and alcoholic cirrhosis.J Pathol. 1998 Sep;186(1):82-9. doi: 10.1002/(SICI)1096-9896(199809)186:1<82::AID-PATH151>3.0.CO;2-D. J Pathol. 1998. PMID: 9875144
-
Enhanced production of macrophage inhibitory protein-1alpha in patients with Behçet's disease.Scand J Rheumatol. 2005 Mar-Apr;34(2):129-35. doi: 10.1080/03009740410006943. Scand J Rheumatol. 2005. PMID: 16095009
-
Augmented production of chemokines (monocyte chemotactic protein-1 (MCP-1), macrophage inflammatory protein-1alpha (MIP-1alpha) and MIP-1beta) in patients with systemic sclerosis: MCP-1 and MIP-1alpha may be involved in the development of pulmonary fibrosis.Clin Exp Immunol. 1999 Jul;117(1):159-65. doi: 10.1046/j.1365-2249.1999.00929.x. Clin Exp Immunol. 1999. PMID: 10403930 Free PMC article.
-
Mechanistic Insights into the Role of MCP-1 in Diverse Liver Pathological Conditions: A Recent Update.Curr Pharm Des. 2025 Mar 3;31(15):1167-1179. doi: 10.2174/0113816128332969241120030733. Curr Pharm Des. 2025. PMID: 39779567 Review.
-
Neutrophilic infiltration in alcoholic hepatitis.Alcohol. 2002 May;27(1):17-21. doi: 10.1016/s0741-8329(02)00206-9. Alcohol. 2002. PMID: 12062632 Review.
Cited by
-
HIV infection is associated with higher levels of monocyte chemoattractant protein-1 and eotaxin among people with recent hepatitis C virus infection.BMC Infect Dis. 2016 Jun 1;16:241. doi: 10.1186/s12879-016-1567-2. BMC Infect Dis. 2016. PMID: 27246604 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
Identification, sequence characterization, and analysis of expression profiles of three novel CC chemokines from domestic duck (Anas platyrhynchos).Immunogenetics. 2005 Jun;57(5):364-73. doi: 10.1007/s00251-005-0796-0. Epub 2005 Apr 20. Immunogenetics. 2005. PMID: 15841394
-
Targeting inflammation for the treatment of alcoholic liver disease.Pharmacol Ther. 2017 Dec;180:77-89. doi: 10.1016/j.pharmthera.2017.06.007. Epub 2017 Jun 19. Pharmacol Ther. 2017. PMID: 28642119 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Identification of serum monocyte chemoattractant protein-1 and prolactin as potential tumor markers in hepatocellular carcinoma.PLoS One. 2013 Jul 18;8(7):e68904. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0068904. Print 2013. PLoS One. 2013. PMID: 23874805 Free PMC article.
-
Increased Sensitivity to Binge Alcohol-Induced Gut Leakiness and Inflammatory Liver Disease in HIV Transgenic Rats.PLoS One. 2015 Oct 20;10(10):e0140498. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0140498. eCollection 2015. PLoS One. 2015. PMID: 26484872 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous
