Administration of interleukin-12 exerts a therapeutic instead of a long-term preventive effect on mite Der p I allergen-induced animal model of airway inflammation
- PMID: 10447737
- PMCID: PMC2326828
- DOI: 10.1046/j.1365-2567.1999.00768.x
Administration of interleukin-12 exerts a therapeutic instead of a long-term preventive effect on mite Der p I allergen-induced animal model of airway inflammation
Abstract
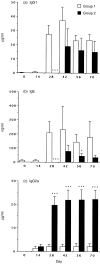
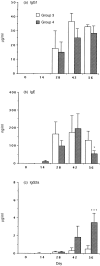
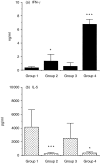
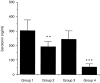
Interleukin-12 (IL-12) is a key cytokine, which promotes T helper type 1 (Th1) cell-mediated immunity and inhibits Th2-type responses. It has been previously shown that IL-12 administration during active immunization following a single allergen exposure can prevent antigen-induced increases in immunoglobulin E (IgE) formation, Th2 cytokine production and bronchoalveolar lavage (BAL) eosinophils in a murine model of allergic airway inflammation. Thus, these studies have now been extended and two IL-12 treatment protocols on this murine model were evaluated. Administration of IL-12 during the active immunization strikingly increased Der p I-specific serum IgG2a and transiently decreased the levels of IgG1 and IgE antibodies following multiple allergen challenges. Such early treatment of IL-12 down-regulated IL-5 production and modestly up-regulated interferon-gamma production but did not effect BAL eosinophilia. These results suggest that repeated exposure to antigen and IL-12 is necessary to maintain a persistent Th1-recall response. Furthermore, administration of IL-12 to actively immunized mice, in which Th2-associated responses were established, had a significant effect on IgG2a synthesis and a modest effect on IgE levels, also down-regulation of IL-5 production, and markedly increased interferon-gamma production and abolished recruitment of eosinophils. Therefore, these data indicate that IL-12 can inhibit antigen-induced eosinophil infiltration into airways, despite the existence of a Th2-associated response. Taken together, these studies suggest that IL-12 may be useful as an immunotherapeutic agent in the treatment of such pulmonary allergic disorders as bronchial asthma.
Figures


References
-
- Voorhorst R, Spieksma-Boezeman MIA, Spieksma FTM. Is a mite (Dermatophagoides sp) the producer of the house dust allergen? Allergy Asthma. 1964;10:329. - PubMed
-
- Krillis S, Baldo BA, Basten A. Antigens and allergens from the common house dust mite Dermatophagoides pteronyssinus. Part II. Identification of the major IgE binding antigen by crossed radioimmunoelectrophoresis. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 1984;74:142. - PubMed
-
- Platts-Mills TA, Snajdr MJ, Ishizaka K, Frankland AW. Measurement of IgE antibody by an antigen-binding assay: correlation with PK activity and IgG and IgA antibodies to allergens. J Immunol. 1978;120:1201. - PubMed
-
- Desreumaux P, Capron M. Eosinophils in allergic reactions. Curr Opin Immunol. 1996;8:790. - PubMed
-
- Busse WW, Calhoun WF, Sedgwick JD. Mechanism of airway inflammation in asthma. Am Rev Respir Dis. 1993;147:20. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

