Ly49A inhibitory receptors redistribute on natural killer cells during target cell interaction
- PMID: 10447751
- PMCID: PMC2326823
- DOI: 10.1046/j.1365-2567.1999.00800.x
Ly49A inhibitory receptors redistribute on natural killer cells during target cell interaction
Abstract
When T effector cells meet antigen-bearing target cells, there is a specific accumulation of T-cell receptors, co-receptors and structural proteins at the point of cell-cell contact. Ly49 inhibitory receptors bind to murine major histocompatibility complex (MHC) class I molecules and prevent natural killer-(NK) cell cytotoxicity. In this study we have tested whether inhibitory receptors accumulate at the point of cell-cell contact when NK cells encounter target cells bearing MHC class I ligands for those inhibitory receptors. We have used RNK-16 effector cells that express Ly49A receptors and have found that there was a specific accumulation of Ly49A receptors at the point of NK cell-target cell contact when the target cells expressed H-2Dd. We also observed that engagement of Ly49A on NK cells resulted in an altered redistribution of potential triggering receptors CD2 and NKR-P1. These data indicate that inhibitory receptors, like activating receptors, may specifically aggregate at the point of cell-cell contact which may be necessary for them to mediate their full inhibitory effect.
Figures

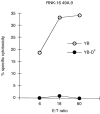
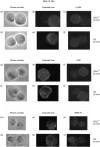
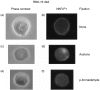
References
-
- Gumperz JE, Parham P. The enigma of the natural killer cell. Nature. 1995;378:245. - PubMed
-
- Lanier LL. Natural killer cell receptors and MHC class I interactions. Curr Opin Immunol. 1997;9:126. - PubMed
-
- Yokoyama WM. Natural killer cell receptors. Curr Opin Immunol. 1998;10:298. - PubMed
-
- Yokoyama WM. Natural killer cell receptors. Curr Opin Immunol. 1995;7:110. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

