Enterobacterial infection modulates major histocompatibility complex class I expression on mononuclear cells
- PMID: 10447763
- PMCID: PMC2326857
- DOI: 10.1046/j.1365-2567.1999.00803.x
Enterobacterial infection modulates major histocompatibility complex class I expression on mononuclear cells
Abstract
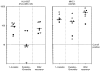
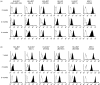
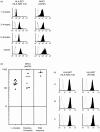
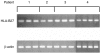
Major histocompatibility complex (MHC) class I expression is reduced in several viral infections, but it is not known whether the same happens during infections caused by intracellular enterobacteria. In this study, the expression of MHC class I antigens on peripheral blood mononuclear cells (PBMC) from 16 patients with Salmonella, Yersinia, or Klebsiella infection was investigated. During or after the acute infection, the expression of MHC class I antigens was markedly decreased in eight patients, all with genotype HLA-B27, and six out of eight with reactive arthritis (ReA). A significant decrease of monomorphic MHC class I was found in three patients, of HLA-B27 in eight (P<0.05) and of HLA-A2 in two. However, patients negative for the HLA-B27 genotype, or healthy HLA-B27-positive individuals, did not have a significant decrease of MHC class I antigens. During the decreased expression on the cell surface, intracellular retention of MHC class I antigens was observed, whereas HLA-B27 mRNA levels did not vary significantly. This is the first evidence that enterobacterial infection may down-regulate expression of MHC class I molecules in vivo and that down-regulation is predominant in patients with the HLA-B27 genotype.
Figures


References
-
- Garrido F, Ruiz-Cabello F, Cabrera T, et al. Implications for immunosurveillance of altered HLA class I phenotypes in human tumours. Immunol Today. 1997;18:89. - PubMed
-
- Andersson M, Pääbo S, Nilsson T, et al. Impaired intracellular transport of class I MHC antigens as a possible means for adenoviruses to evade immune surveillance. Cell. 1985;43:215. - PubMed
-
- Hill AB, Barnett BC, McMichael AJ, et al. HLA class I molecules are not transported to the cell surface in cells infected with herpes simplex virus types 1 and 2. J Immunol. 1994;152:2736. - PubMed
-
- Ploegh HL. Viral strategies of immune evasion. Science. 1998;280:248. - PubMed
-
- Sieper J, Braun J. Pathogenesis of spondylarthropathies. Persistent antigen, autoimmunity, or both? Arthritis Rheum. 1995;38:1547. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

