Intravenous tolerization with type II collagen induces interleukin-4-and interleukin-10-producing CD4+ T cells
- PMID: 10447769
- PMCID: PMC2326845
- DOI: 10.1046/j.1365-2567.1999.00778.x
Intravenous tolerization with type II collagen induces interleukin-4-and interleukin-10-producing CD4+ T cells
Abstract
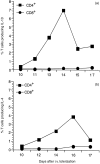
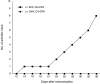
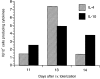
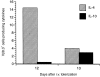
Intravenous (i.v.) administration of type II collagen (CII) is an effective way to induce tolerance and suppress disease in the collagen-induced arthritis (CIA) model. In this study, we demonstrated that a single i.v. dose of CII (as low as 0.1 mg/mouse) completely prevented the development of CIA. This suppression was accompanied by decreases in levels of antibody specific for the immunogen, bovine CII and autoantigen, mouse CII. Splenocytes obtained from CII-tolerized mice and stimulated with CII in vitro produced predominantly the T helper 2 (Th2)-type cytokines interleukin-4 (IL-4) and interleukin-10 (IL-10). In contrast, cells obtained from mice immunized with CII produced predominantly interferon-gamma (IFN-gamma). Two-colour flow cytometric analysis of cytokine expression and T-cell phenotype demonstrated that CD4+ cells and not CD8+ or gammadelta+ cells were the predominant regulatory cells producing IL-4 and IL-10. Transgenic mice bearing a T-cell receptor (TCR) specific for CII had a greater increase in the number of IL-4-secreting CD4+ cells, as well as a marked increase of IL-4 in culture supernatants. This cytokine was produced by transgene-bearing T cells. Elucidation of mechanisms for the induction of tolerance in mature T cells is an important line of study in autoimmune models because of the potential application for treating organ-specific autoimmune disease.
Figures
References
-
- Cremer MA, Hernandez AD, Stuart JM, Townes AS, Kang AH. Collagen-induced arthritis in rats: antigen specific suppression of arthritis and immunity by intravenously injected native type II collagen. J Immunol. 1983;131:2995. - PubMed
-
- Wooley PH, Luthra HS, Singh S, Huse A, Stuart JM, David CS. Passive transfer of arthritis in mice by human anti-type II collagen antibody. Mayo Clinic Proc. 1984;59:737. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials

