Characterization of selective resistance to insulin signaling in the vasculature of obese Zucker (fa/fa) rats
- PMID: 10449437
- PMCID: PMC408521
- DOI: 10.1172/JCI5971
Characterization of selective resistance to insulin signaling in the vasculature of obese Zucker (fa/fa) rats
Abstract
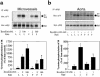
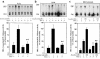
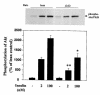
Both insulin resistance and hyperinsulinemia have been reported to be independent risk factors for cardiovascular diseases. However, little is known regarding insulin signaling in the vascular tissues in insulin-resistant states. In this report, insulin signaling on the phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase (PI 3-kinase) and mitogen-activated protein (MAP) kinase pathways were compared in vascular tissues of lean and obese Zucker (fa/fa) rats in both ex vivo and in vivo studies. Ex vivo, insulin-stimulated tyrosine phosphorylation of insulin receptor beta subunits (IRbeta) in the aorta and microvessels of obese rats was significantly decreased compared with lean rats, although the protein levels of IRbeta in the 2 groups were not different. Insulin-induced tyrosine phosphorylation of insulin receptor substrates 1 and 2 (IRS-1 and IRS-2) and their protein levels were decreased in the aorta of obese rats compared with lean rats. The association of p85 subunit to the IRS proteins and the IRS-associated PI 3-kinase activities stimulated by insulin in the aorta of obese rats were significantly decreased compared with the lean rats. In addition, insulin-stimulated serine phosphorylation of Akt, a downstream kinase of PI 3-kinase pathway, was also reduced significantly in isolated microvessels from obese rats compared with the lean rats. In euglycemic clamp studies, insulin infusion greatly increased tyrosine phosphorylation of IRbeta- and IRS-2-associated PI 3-kinase activity in the aorta of lean rats, but only slight increases were observed in obese rats. In contrast, insulin stimulated tyrosine phosphorylation of MAP kinase (ERK-1/2) equally in isolated microvessels of lean and obese rats, although basal tyrosine phosphorylation of ERK-1/2 was higher in the obese rats. To our knowledge, these data provided the first direct measurements of insulin signaling in the vascular tissues, and documented a selective resistance to PI 3-kinase (but not to MAP kinase pathway) in the vascular tissues of obese Zucker rats.
Figures


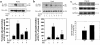


References
-
- Obata T, et al. Insulin signaling and its regulation of system A amino acid uptake in cultured rat vascular smooth muscle cells. Circ Res. 1996;79:1167–1176. - PubMed
-
- Tamaroglio TA, Lo CS. Regulation of fibronectin by insulin-like growth factor-1 in cultured rat thoracic smooth muscle cells and glomerular mesangial cells. Exp Cell Res. 1994;21:338–346. - PubMed
-
- Anderson PW, et al. Insulin and angiotensin II are additive in stimulating TGFβ 1 and matrix mRNAs in mesangial cells. Kidney Int. 1996;50:745–753. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

