Phylogenetic analysis of Rhinosporidium seeberi's 18S small-subunit ribosomal DNA groups this pathogen among members of the protoctistan Mesomycetozoa clade
- PMID: 10449446
- PMCID: PMC85368
- DOI: 10.1128/JCM.37.9.2750-2754.1999
Phylogenetic analysis of Rhinosporidium seeberi's 18S small-subunit ribosomal DNA groups this pathogen among members of the protoctistan Mesomycetozoa clade
Abstract
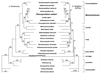
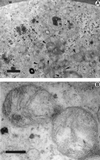
For the past 100 years the phylogenetic affinities of Rhinosporidium seeberi have been controversial. Based on its morphological features, it has been classified as a protozoan or as a member of the kingdom Fungi. We have amplified and sequenced nearly a full-length 18S small-subunit (SSU) ribosomal DNA (rDNA) sequence from R. seeberi. Using phylogenetic analysis, by parsimony and distance methods, of R. seeberi's 18S SSU rDNA and that of other eukaryotes, we found that this enigmatic pathogen of humans and animals clusters with a novel group of fish parasites referred to as the DRIP clade (Dermocystidium, rossete agent, Ichthyophonus, and Psorospermium), near the animal-fungal divergence. Our phylogenetic analyses also indicate that R. seeberi is the sister taxon of the two Dermocystidium species used in this study. This molecular affinity is remarkable since members of the genus Dermocystidium form spherical structures in infected hosts, produce endospores, have not been cultured, and possess mitochondria with flat cristae. With the addition of R. seeberi to this clade, the acronym DRIP is no longer appropriate. We propose to name this monophyletic clade Mesomycetozoa to reflect the group's phylogenetic association within the Eucarya.
Figures
References
-
- Ahluwalia K B, Maheshwari N, Deka R C. Rhinosporidiosis: a study that resolves etiologic controversies. Am J Rhinol. 1997;11:479–483. - PubMed
-
- Ahluwalia K B. New interpretations in rhinosporidiosis, enigmatic disease of the last nine decades. J Submicrosc Cytol Pathol. 1992;24:109–114. - PubMed
-
- Ajello L. Ecology and epidemiology of hydrophilic infectious fungi and parafungi of medical mycologycal importance: a new category of pathogens. In: Ajello L, Hay R J, editors. Topley & Wilson’s microbiology and microbial infections. 9th ed. Vol. 4. London, England: Arnold; 1998. pp. 67–73.
-
- Arsecularatne S N, Ajello L. Rhinosporidium seeberi. In: Ajello L, Hay R J, editors. Topley & Wilson’s microbiology and microbial infections. 9th ed. Vol. 4. London, England: Arnold; 1998. pp. 596–615.
-
- Ashworth J H. On Rhinosporidium seeberi (Wernicke, 1903) with special reference to its sporulation and affinities. Trans R Soc Edinb. 1923;53:301–342.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
- Actions
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

