Phenotypic and genetic characterization of a novel Borrelia burgdorferi sensu lato isolate from a patient with lyme borreliosis
- PMID: 10449497
- PMCID: PMC85444
- DOI: 10.1128/JCM.37.9.3025-3028.1999
Phenotypic and genetic characterization of a novel Borrelia burgdorferi sensu lato isolate from a patient with lyme borreliosis
Abstract
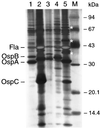
Borrelia burgdorferi sensu lato A14S was cultured from a skin biopsy specimen of a patient with erythema migrans in The Netherlands. This isolate had a unique DNA fingerprint pattern compared to 135 other B. burgdorferi sensu lato isolates. In this study, the isolate A14S was further characterized by protein analysis with sodium dodecyl sulfate-polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis (SDS-PAGE) and reactivity with various monoclonal antibodies. In addition, the 16S rRNA, ospA, and ospC genes, as well as the 5S-23S rRNA intergenic spacer DNA, were amplified by PCR, cloned, and sequenced. SDS-PAGE protein profiles and phylogenetic analysis based on all of the analyzed genes confirmed that B. burgdorferi sensu lato A14S was phenotypically and genetically different from the three human pathogenic species B. burgdorferi sensu stricto, Borrelia garinii, and Borrelia afzelii, as well as from other B. burgdorferi sensu lato species. Our findings indicate that Borrelia genomic groups or isolates other than the three well-known human pathogenic species may also cause human Lyme borreliosis.
Figures


References
-
- Baranton G, Postic D, Saint Girons I, Boerlin P, Piffaretti J C, Assous M, Grimont P A. Delineation of Borrelia burgdorferi sensu stricto, Borrelia garinii sp. nov., and group VS461 associated with Lyme borreliosis. Int J Syst Bacteriol. 1992;42:378–383. - PubMed
-
- Canica M M, Nato F, du Merle L, Mazie J C, Baranton G, Postic D. Monoclonal antibodies for identification of Borrelia afzelii sp. nov. associated with late cutaneous manifestations of Lyme borreliosis. Scand J Infect Dis. 1993;25:441–448. - PubMed
-
- Fukunaga M, Hamase A, Okada K, Inoue H, Tsuruta Y, Miyamoto K, Nakao M. Characterization of spirochetes isolated from ticks (Ixodes tanuki, Ixodes turdus, and Ixodes columnae) and comparison of the sequences with those of Borrelia burgdorferi sensu lato strains. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1996;62:2338–2344. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Fukunaga M, Hamase A, Okada K, Nakao M. Borrelia tanukii sp. nov. and Borrelia turdae sp. nov. found from ixodid ticks in Japan: rapid species identification by 16S rRNA gene-targeted PCR analysis. Microbiol Immunol. 1996;40:877–881. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases

