The major receptor for C-reactive protein on leukocytes is fcgamma receptor II
- PMID: 10449529
- PMCID: PMC2195602
- DOI: 10.1084/jem.190.4.585
The major receptor for C-reactive protein on leukocytes is fcgamma receptor II
Abstract
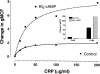
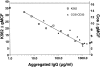
C-reactive protein (CRP) is an acute phase serum protein that shares several functions with immunoglobulin (Ig)G including complement activation and binding to receptors on monocytes and neutrophils. The identity of the receptor for CRP has been the target of extensive research. We previously determined that CRP binds to the high affinity receptor for IgG, FcgammaRI (CD64). However, this interaction could not account for the majority of binding of CRP to neutrophils or monocytic cells. We now determine that CRP also interacts with FcgammaRIIa (CD32), the low affinity receptor for IgG on monocytes and neutrophils. COS-7 cells were transfected with a construct containing the human FcgammaRIIA cDNA. CRP binding and the presence of CD32 were detected by mAb and analyzed by two-color flow cytometry. Cells expressing CD32 bound CRP in a dose-dependent and saturable manner consistent with receptor binding. CRP bound to transfectants and K-562 cells with similar kinetics, and in both cases binding was completely inhibited by aggregated IgG. On monocytic cell lines, treatment with Bt(2)cAMP increased FcgammaRII expression and enhanced CRP binding. CRP also specifically precipitated FcgammaRI and FcgammaRII from the monocytic cell line, THP-1. It is suggested that the major receptor for CRP on phagocytic cells is FcgammaRII.
Figures



References
-
- Kaplan M.H., Volanakis J.E. Interactions of C-reactive protein with the complement system. I. Consumption of human complement associated with the reaction of C-reactive protein with pneumococcal polysaccharide and with the choline phosphatides, lecithin and sphingomyelin. J. Immunol. 1974;112:2135–2147. - PubMed
-
- Mortensen R.F., Osmand A.P., Lint T.F., Gewurz H. Interaction of C-reactive protein with lymphocytes and monocytescomplement-dependent adherence and phagocytosis. J. Immunol. 1976;117:774–781. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

