Phosphorylated tau can promote tubulin assembly
- PMID: 10449722
- PMCID: PMC22238
- DOI: 10.1073/pnas.96.17.9503
Phosphorylated tau can promote tubulin assembly
Abstract
Phosphorylation can affect the function of microtubule-associated protein tau. Here, the human brain tau with 441 amino acids was phosphorylated by cyclic-AMP-dependent protein kinase (PKA) or glycogen synthase kinase-3beta. PKA-phosphorylated tau (2.7 mol phosphates/mol) does not promote tubulin assembly as judged by spectrophotometric and atomic force microscopy measurements, unless trimethylamine N-oxide (TMAO), a natural occurring osmolyte, is included in these assays. TMAO is also found to promote tubulin assembly of glycogen synthase kinase-3beta-phosphorylated tau (1.6 mol phosphates/mol). TMAO does not act by causing a chemical dephosphorylation of phosphorylated tau, but it acts to overcome the functional deficit caused by phosphorylation. PKA-phosphorylated tau binds to tubulin in the presence of TMAO and lowers the critical concentration of tubulin needed for assembly. From these data, we conclude that PKA-phosphorylated tau retains the ability to bind tubulin and promote tubulin assembly. TMAO is required, however, to sensitize the reaction. Possible uses of TMAO in relation to studies of tubulin assembly in vitro, in intact cells, and in relation to Alzheimer's disease are presented in this report.
Figures
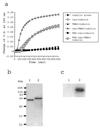
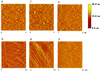
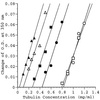
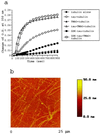
References
-
- Iqbal K, Grundke-Iqbal I, Zaidi T, Merz P A, Wen G Y, Shaikh S S, Wisniewski H M, Alzfuzoff I, Winblad B. Lancet. 1986;2:421–426. - PubMed
-
- Mandelkow E-M, Mandelkow E. Trends Biochem Sci. 1993;18:480–483. - PubMed
-
- Goedert M. Trends Neurosci. 1993;16:460–465. - PubMed
-
- Schneider A, Biernat J, von Bergen M, Mandelkow E, Mandelkow E-M. Biochemistry. 1999;38:3549–3558. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

