Folding of a large ribozyme during transcription and the effect of the elongation factor NusA
- PMID: 10449729
- PMCID: PMC22245
- DOI: 10.1073/pnas.96.17.9545
Folding of a large ribozyme during transcription and the effect of the elongation factor NusA
Abstract
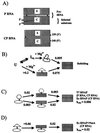
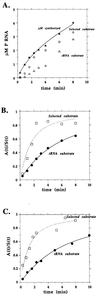
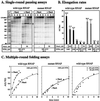
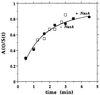
We compared in vitro transcription-initiated folding of the ribozyme from Bacillus subtilis RNase P to refolding from the full-length, denatured state by monitoring the appearance of its catalytic activity. At 37 degrees C, Mg(2+)-initiated refolding of the wild type and a circularly permutate ribozyme takes minutes and is limited by a kinetic trap. Transcription by T7 RNA polymerase alters the folding pathway of both RNAs and introduces new kinetic traps. Transcription by the core Escherichia coli RNA polymerase yields the same result, in spite of its 4-fold-slower elongation rate. However, the presence of its elongation factor NusA accelerates more than 10-fold the transcription-initiated folding of the circularly, permutated ribozyme by E. coli RNA polymerase. The effect of NusA likely is caused by its enhancement of transcriptional pausing because NusA did not accelerate transcription-initiated folding using a mutant RNA polymerase that failed to pause or respond to NusA during ribozyme synthesis. We conclude that both transcription and specific pausing therein can alter RNA-folding pathways.
Figures
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

