Redox-linked transient deprotonation at the binuclear site in the aa(3)-type quinol oxidase from Acidianus ambivalens: implications for proton translocation
- PMID: 10449737
- PMCID: PMC22253
- DOI: 10.1073/pnas.96.17.9591
Redox-linked transient deprotonation at the binuclear site in the aa(3)-type quinol oxidase from Acidianus ambivalens: implications for proton translocation
Abstract
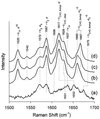
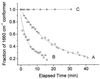
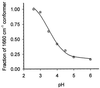
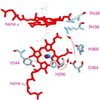
The hyperthermophilic archaeon Acidianus ambivalens expresses a membrane-bound aa(3)-type quinol oxidase, when grown aerobically, that we have studied by resonance Raman spectroscopy. The purified aa(3) oxidase, which does not contain bound quinol, undergoes a reversible slow conformational change at heme a(3) upon reduction, as indicated by a change in the frequency of its heme formyl stretching mode, from 1,660 cm(-1) to 1,667 cm(-1). In contrast, upon reduction of the integral membrane enzyme or the purified enzyme preincubated with decylubiquinol, this mode appears at 1,667 cm(-1) much more rapidly, suggesting a role of the bound quinol in controlling the redox-linked conformational changes. The shift of the formyl mode to higher frequency is attributed to a loss of hydrogen bonding that is associated with a group having a pKa of approximately 3.8. Based on these observations, a crucial element for proton translocation involving a redox-linked conformational change near the heme a(3) formyl group is postulated.
Figures

References
-
- Anemuller S, Schmidt C L, Pacheco I, Schafer G, Teixeira M. FEMS Microbiol Lett. 1994;117:275–280.
-
- Schafer G. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1996;1277:163–200. - PubMed
-
- Zillig W, Yeats S, Holz I, Bock A, Gropp F, Rettenberger M, Lutz S. Nature (London) 1985;313:789–791. - PubMed
-
- Fuchs T, Huber H, Burggraf S, Stetter K O. Syst Appl Microbiol. 1996;19:56–60.
-
- Giuffre A, Gomes C M, Antonini G, D’Itri E, Teixeira M, Brunori M. Eur J Biochem. 1997;250:383–388. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

