Human eosinophils regulate human lung- and skin-derived fibroblast properties in vitro: a role for transforming growth factor beta (TGF-beta)
- PMID: 10449750
- PMCID: PMC22266
- DOI: 10.1073/pnas.96.17.9660
Human eosinophils regulate human lung- and skin-derived fibroblast properties in vitro: a role for transforming growth factor beta (TGF-beta)
Abstract
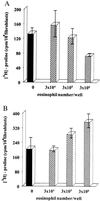
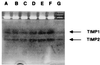
Eosinophils have been associated with fibrosis. To investigate their direct role in fibrosis, human peripheral blood eosinophil sonicate was added to human lung or dermal fibroblasts, and proliferation ([(3)H]thymidine) and collagen synthesis ([(3)H]proline) were evaluated. Proliferation was enhanced significantly in the monolayers in a dose-dependent manner. The activity of the eosinophil fibrogenic factor(s) remained unaltered when heated (56 degrees C, 30 min). Supernatants of cultured eosinophils (20 min or 18 hr) also enhanced lung fibroblast proliferation, indicating that the preformed mitogenic factor(s) can be released both promptly and with a long kinetic. Eosinophils significantly decreased collagen production in lung fibroblasts while increasing it in dermal fibroblasts. However, eosinophils containing matrix metalloproteinase 9 (zymography) in latent form and tissue inhibitors of metalloproteinases 1 and 2 (reverse zymography) did not influence either fibroblast matrix metalloproteinases or tissue inhibitors of metalloproteinases. Eosinophil sonicate added to skin and lung fibroblasts in tridimensional collagen lattices significantly enhanced lattice contraction. Transforming growth factor beta (TGF-beta) is a major fibrogenic cytokine produced by eosinophils. Therefore, to assess its role, eosinophil sonicate was preincubated with anti-TGF-beta neutralizing antibodies. This treatment partially inhibited proliferation of lung and collagen synthesis of dermal fibroblasts and suppressed the stimulation of lattice contraction, indicating the fibrogenic role of eosinophil-associated TGF-beta. In conclusion, we have shown that eosinophils act as direct modulatory cells in fibroblast proliferation, collagen synthesis, and lattice contraction, in part, through TGF-beta. These data corroborate the importance of eosinophils in skin and lung fibrosis.
Figures


References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

