An inverse relationship between T cell receptor affinity and antigen dose during CD4(+) T cell responses in vivo and in vitro
- PMID: 10449771
- PMCID: PMC22287
- DOI: 10.1073/pnas.96.17.9781
An inverse relationship between T cell receptor affinity and antigen dose during CD4(+) T cell responses in vivo and in vitro
Abstract
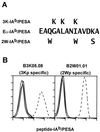
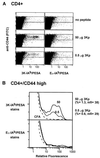
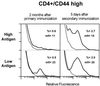
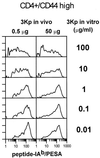
Multimeric peptide/class II MHC staining reagents were synthesized and shown to bind with appropriate specificity to T cell hybridomas. A small, expanded population of T cells detected with one of these reagents in peptide-immunized C57BL/10 mice persisted for several months. This population expanded further on secondary immunization. Equating the extent of binding of this reagent to T cell receptor affinity, we saw little correlation of immunizing peptide dose to T cell receptor affinity at the peak of the primary response. However, there was an inverse relation between peptide dose and the apparent receptor affinity of the T cells that were present several months after a primary response or after a secondary stimulation either in vivo or in vitro.
Figures
References
-
- Garboczi D N, Utz U, Ghosh P, Seth A, Kim J, VanTienhoven E A, Biddison W E, Wiley D C. J Immunol. 1996;157:5403–5410. - PubMed
-
- Kozono H, White J, Clements J, Marrack P, Kappler J. Nature (London) 1994;369:151–154. - PubMed
-
- Ignatowicz L, Winslow G, Bill J, Kappler J, Marrack P. J Immunol. 1995;154:3852–3862. - PubMed
-
- Altman J D, Moss P A H, Goulder P J R, Barouch D H, McHeyzer-Williams M G, Bell J I, McMichael A J, Davis M M. Science. 1996;274:94–96. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials

