Different training procedures recruit either one or two critical periods for contextual memory consolidation, each of which requires protein synthesis and PKA
- PMID: 10454361
- PMCID: PMC311273
Different training procedures recruit either one or two critical periods for contextual memory consolidation, each of which requires protein synthesis and PKA
Abstract
We have used a combined genetic and pharmacological approach to define the time course of the requirement for protein kinase A (PKA) and protein synthesis in long-term memory for contextual fear conditioning in mice. The time course of amnesia in transgenic mice that express R(AB) and have genetically reduced PKA activity in the hippocampus parallels that observed both in mice treated with inhibitors of PKA and mice treated with inhibitors of protein synthesis. This PKA- and protein synthesis-dependent memory develops between 1 hr and 3 hr after training. By injecting the protein synthesis inhibitor anisomycin or the PKA inhibitor Rp-cAMPs at various times after training, we find that depending on the nature of training, contextual memory has either one or two brief consolidation periods requiring synthesis of new proteins, and each of these also requires PKA. Weak training shows two time periods of sensitivity to inhibitors of protein synthesis and PKA, whereas stronger training exhibits only one. These studies underscore the parallel dependence of long-term contextual memory on protein synthesis and PKA and suggest that different training protocols may recruit a common signaling pathway in distinct ways.
Figures

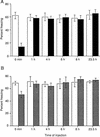

References
-
- Abel T, Nguyen P, Barad M, Deuel T, Kandel ER, Bourtchouladze R. Genetic demonstration of a role for PKA in the late phase of LTP in the hippocampus-based long-term memory. Cell. 1997;88:615–626. - PubMed
-
- Abraham WC, Mason SE, Demmer J, Williams JM, Richardson C, Tate W, Lawlor PA, Dragunow M. Correlation between immediate early gene induction and the persistence of long-term potentiation. Neuroscience. 1993;56:717–727. - PubMed
-
- Barondes SH, Cohen HD. Puromycin effect on successive phases of memory storage. Science. 1966;151:594–595. - PubMed
-
- Barracco RA, Stettner LJ. Antibiotics and memory. Psychol Bull. 1976;83:242–302. - PubMed
-
- Barzilai A, Kennnedy TE, Sweat JD, Kandel ER. 5-HT modulates protein synthesis and the expression of specific proteins during long-term facilitation in Aplysia sensory neurons. Neuron. 1989;2:1577–1586. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
