Targeted expression of the DNA binding domain of DRE-binding factor, a Drosophila transcription factor, attenuates DNA replication of the salivary gland and eye imaginal disc
- PMID: 10454549
- PMCID: PMC84493
- DOI: 10.1128/MCB.19.9.6020
Targeted expression of the DNA binding domain of DRE-binding factor, a Drosophila transcription factor, attenuates DNA replication of the salivary gland and eye imaginal disc
Abstract
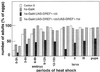
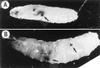
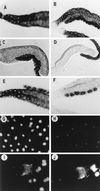
The promoters of Drosophila genes encoding DNA replication-related proteins contain transcription regulatory elements consisting of an 8-bp palindromic DNA replication-related element (DRE) sequence (5'-TATCGATA). The specific DRE-binding factor (DREF), a homodimer of the polypeptide with 709 amino acid residues, is a positive trans-acting factor for transcription of DRE-containing genes. Both DRE binding and dimer formation are associated with residues 16 to 115 of the N-terminal region. We have established transgenic flies expressing the full-length DREF polypeptide or its N-terminal fragment (amino acid residues 1 to 125) under the control of the heat shock promoter, the salivary gland-specific promoter, or the eye imaginal disc-specific promoter. Heat shock induction of the N-terminal fragment during embryonic, larval, or pupal stages caused greater than 50% lethality. This lethality was overcome by coexpression of the full-length DREF. In salivary glands of the transgenic larvae expressing the N-terminal fragment, this fragment formed a homodimer and a heterodimer with the endogenous DREF. Ectopic expression of the N-terminal fragment in salivary gland cells reduced the contents of mRNAs for the 180-kDa subunit of DNA polymerase alpha and for dE2F and the extent of DNA endoreplication. Ectopic expression of the N-terminal fragment in the eye imaginal discs significantly reduced DNA replication in cells at the second mitotic wave. The lines of evidence suggest that the N-terminal fragment can impede the endogenous DREF function in a dominant negative manner and that DREF is required for normal DNA replication in both mitotic cell cycle and endo cycle.
Figures



Similar articles
-
The DRE/DREF transcriptional regulatory system: a master key for cell proliferation.Biochim Biophys Acta. 2008 Feb;1779(2):81-9. doi: 10.1016/j.bbagrm.2007.11.011. Epub 2007 Dec 4. Biochim Biophys Acta. 2008. PMID: 18155677 Review.
-
Ectopic expression of DREF induces DNA synthesis, apoptosis, and unusual morphogenesis in the Drosophila eye imaginal disc: possible interaction with Polycomb and trithorax group proteins.Mol Cell Biol. 2001 Nov;21(21):7231-42. doi: 10.1128/MCB.21.21.7231-7242.2001. Mol Cell Biol. 2001. PMID: 11585906 Free PMC article.
-
The DNA replication-related element (DRE)/DRE-binding factor system is a transcriptional regulator of the Drosophila E2F gene.J Biol Chem. 1998 Oct 2;273(40):26042-51. doi: 10.1074/jbc.273.40.26042. J Biol Chem. 1998. PMID: 9748283
-
Transcriptional regulation of the Drosophila ANT gene by the DRE/DREF system.Genes Cells. 2007 May;12(5):569-79. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2443.2007.01075.x. Genes Cells. 2007. PMID: 17535248
-
Novel 8-base pair sequence (Drosophila DNA replication-related element) and specific binding factor involved in the expression of Drosophila genes for DNA polymerase alpha and proliferating cell nuclear antigen.J Biol Chem. 1993 Jan 25;268(3):2092-9. J Biol Chem. 1993. PMID: 8093616
Cited by
-
Dynamic changes in the genomic localization of DNA replication-related element binding factor during the cell cycle.Cell Cycle. 2013 May 15;12(10):1605-15. doi: 10.4161/cc.24742. Epub 2013 Apr 25. Cell Cycle. 2013. PMID: 23624840 Free PMC article.
-
hDREF regulates cell proliferation and expression of ribosomal protein genes.Mol Cell Biol. 2007 Mar;27(6):2003-13. doi: 10.1128/MCB.01462-06. Epub 2007 Jan 12. Mol Cell Biol. 2007. PMID: 17220279 Free PMC article.
-
Genetic screening for modifiers of the DREF pathway in Drosophila melanogaster: identification and characterization of HP6 as a novel target of DREF.Nucleic Acids Res. 2009 Apr;37(5):1423-37. doi: 10.1093/nar/gkn1068. Epub 2009 Jan 9. Nucleic Acids Res. 2009. PMID: 19136464 Free PMC article.
-
C. elegans BED domain transcription factor BED-3 controls lineage-specific cell proliferation during organogenesis.Dev Biol. 2010 Feb 15;338(2):226-36. doi: 10.1016/j.ydbio.2009.12.005. Epub 2009 Dec 21. Dev Biol. 2010. PMID: 20005870 Free PMC article.
-
The Hippo pathway as a target of the Drosophila DRE/DREF transcriptional regulatory pathway.Sci Rep. 2014 Nov 26;4:7196. doi: 10.1038/srep07196. Sci Rep. 2014. PMID: 25424907 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Brand A, Perrimon N. Targeted gene expression as a means of altering cell fates and generating dominant phenotype. Development. 1993;118:401–415. - PubMed
-
- Brand A, Perrimon N. Raf acts downstream of the EGF receptor to determine dorso-ventral polarity during Drosophila oogenesis. Genes Dev. 1994;8:629–639. - PubMed
-
- Cox K H, DeLeon D Y, Angerer L M, Angerer R C. Detection of mRNAs in sea urchin embryos by in situ hybridization using asymmetric RNA probes. Dev Biol. 1984;101:485–502. - PubMed
-
- Duronio R J, O’Farrell P H, Xie J E, Brook A, Dyson N. The transcription factor E2F is required for S phase during Drosophila embryogenesis. Genes Dev. 1995;9:1445–1455. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
