A novel role for helix 12 of retinoid X receptor in regulating repression
- PMID: 10454590
- PMCID: PMC84614
- DOI: 10.1128/MCB.19.9.6448
A novel role for helix 12 of retinoid X receptor in regulating repression
Abstract
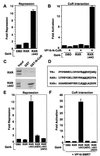
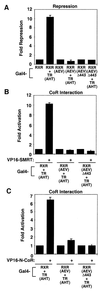
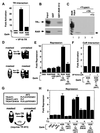
Nutrients, drugs, and hormones influence transcription during differentiation and metabolism by binding to high-affinity nuclear receptors. In the absence of ligand, some but not all nuclear receptors repress transcription as a heterodimer with retinoid X receptor (RXR). Here we define a novel role for helix 12 (H12) in sterically masking the corepressor (CoR) binding site in apo-RXR. Removing H12 converts RXR to a potent transcriptional repressor. The length but not the specific sequence of H12 is critical for masking RXR's intrinsic repression function. This contrasts with the amphipathic character required for mediating ligand-dependent activation and coactivator recruitment. Physiologically, we show that heterodimerization of RXR with apo-thyroid hormone receptor (TR) unmasks the CoR binding site in RXR and allows the TR-RXR heterodimer to repress. A molecular mechanism that involves sequence-specific interaction between RXR H12 and the coactivator-binding surface of the nuclear receptor is proposed for this heterodimerization-mediated unmasking. Peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor gamma does not interact as well with RXR H12, thus explaining its inability to repress transcription as an RXR heterodimer. The requirement to unmask RXR's latent repression function explains why only certain RXR partners repress transcription.
Figures


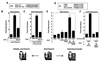

Similar articles
-
Protein-protein interaction domains and the heterodimerization of thyroid hormone receptor variant alpha2 with retinoid X receptors.Mol Endocrinol. 1998 Oct;12(10):1542-50. doi: 10.1210/mend.12.10.0178. Mol Endocrinol. 1998. PMID: 9773977
-
Molecular determinants of nuclear receptor-corepressor interaction.Genes Dev. 1999 Dec 15;13(24):3198-208. doi: 10.1101/gad.13.24.3198. Genes Dev. 1999. PMID: 10617569 Free PMC article.
-
Differential recognition of liganded and unliganded thyroid hormone receptor by retinoid X receptor regulates transcriptional repression.Mol Cell Biol. 1997 Dec;17(12):6887-97. doi: 10.1128/MCB.17.12.6887. Mol Cell Biol. 1997. PMID: 9372920 Free PMC article.
-
The retinoid X receptor and its ligands: versatile regulators of metabolic function, cell differentiation and cell death.J Biol Regul Homeost Agents. 2003 Jan-Mar;17(1):29-45. J Biol Regul Homeost Agents. 2003. PMID: 12757020 Review.
-
Thyroid hormone crosstalk with nuclear receptor signaling in metabolic regulation.Trends Endocrinol Metab. 2010 Mar;21(3):166-73. doi: 10.1016/j.tem.2009.11.004. Epub 2009 Dec 16. Trends Endocrinol Metab. 2010. PMID: 20015660 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Structural mechanism for signal transduction in RXR nuclear receptor heterodimers.Nat Commun. 2015 Aug 20;6:8013. doi: 10.1038/ncomms9013. Nat Commun. 2015. PMID: 26289479 Free PMC article.
-
Alternative mRNA splicing of SMRT creates functional diversity by generating corepressor isoforms with different affinities for different nuclear receptors.J Biol Chem. 2005 Mar 4;280(9):7493-503. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M411514200. Epub 2005 Jan 4. J Biol Chem. 2005. PMID: 15632172 Free PMC article.
-
Ligand-dependent contribution of RXRbeta to cholesterol homeostasis in Sertoli cells.EMBO Rep. 2004 Mar;5(3):285-90. doi: 10.1038/sj.embor.7400094. EMBO Rep. 2004. PMID: 14993927 Free PMC article.
-
CIA, a novel estrogen receptor coactivator with a bifunctional nuclear receptor interacting determinant.Mol Cell Biol. 2001 Jan;21(1):343-53. doi: 10.1128/MCB.21.1.343-353.2001. Mol Cell Biol. 2001. PMID: 11113208 Free PMC article.
-
Structural basis for retinoic X receptor repression on the tetramer.J Biol Chem. 2011 Jul 15;286(28):24593-8. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M111.245498. Epub 2011 May 24. J Biol Chem. 2011. PMID: 21613212 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Allan G F, Leng X, Tsai S Y, Weigel N L, Edwards D P, Tsai M J, O’Malley B W. Hormone and antihormone induce distinct conformational changes which are central to steroid receptor activation. J Biol Chem. 1992;267:19513–19520. - PubMed
-
- Alland L, Muhle R, Hou H, Potes J, Chin L, Schreiber-Agus N, DePinho R A. Role for N-CoR and histone deacetylase in Sin3-mediated transcriptional repression. Nature. 1997;387:49–55. - PubMed
-
- Bourguet W, Ruff M, Chambon P, Gronemeyer H, Moras D. Crystal structure of the ligand-binding domain of the human nuclear receptor RXR-alpha. Nature. 1995;375:377–382. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
