Anti-inflammatory properties of cytochrome P450 epoxygenase-derived eicosanoids
- PMID: 10455056
- PMCID: PMC2720027
- DOI: 10.1126/science.285.5431.1276
Anti-inflammatory properties of cytochrome P450 epoxygenase-derived eicosanoids
Abstract
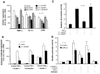
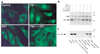
The epoxyeicosatrienoic acids (EETs) are products of cytochrome P450 epoxygenases that have vasodilatory properties similar to that of endothelium-derived hyperpolarizing factor. The cytochrome P450 isoform CYP2J2 was cloned and identified as a potential source of EETs in human endothelial cells. Physiological concentrations of EETs or overexpression of CYP2J2 decreased cytokine-induced endothelial cell adhesion molecule expression, and EETs prevented leukocyte adhesion to the vascular wall by a mechanism involving inhibition of transcription factor NF-kappaB and IkappaB kinase. The inhibitory effects of EETs were independent of their membrane-hyperpolarizing effects, suggesting that these molecules play an important nonvasodilatory role in vascular inflammation.
Figures


References
-
- Capdevila JH, Falck JR, Estabrook RW. FASEB J. 1992;6:731. - PubMed
-
- Campbell WB, Harder DR. Circ. Res. 1999;84:484. - PubMed
-
- Campbell WB, Gebremedhin D, Pratt PF, Harder DR. ibid. 1996;78:415. - PubMed
-
- Rosolowsky M, Campbell WB. Biochim. Biophys. Acta. 1996;1299:267. - PubMed
-
- Oltman CL, Weintraub NL, VanRollins M, Dellsperger KC. Circ. Res. 1998;83:932. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

