Pharmacological characterization of 5-HT4 receptors mediating relaxation of canine isolated rectum circular smooth muscle
- PMID: 10455293
- PMCID: PMC1760667
- DOI: 10.1038/sj.bjp.0702665
Pharmacological characterization of 5-HT4 receptors mediating relaxation of canine isolated rectum circular smooth muscle
Abstract
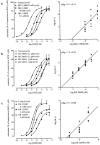
This study aimed to characterize for the first time in vitro 5-HT4 receptors in the canine gastrointestinal tract. For this purpose, we used circular muscle strips of the canine isolated rectum. In the presence of methysergide (60 microM), 5-HT induced relaxation of methacholine (1 microM)-precontracted muscle strips, yielding a monophasic sigmoidal concentration-relaxation curve (pEC50 7.2+/-0.07). Tetrodotoxin (0.3 microM) did not affect the curve to 5-HT, suggesting the inhibitory 5-HT receptor is located on the smooth muscle. Granisetron (0.3 microM) did also not affect the curve to 5-HT, which excludes the 5-HT3 receptor mediating the relaxation to 5-HT. The presence of methysergide rules out the involvement of 5-HT1, 5-HT2 or 5-HT7 receptors. 5-HT, the selective 5-HT4 receptor agonists R076186, prucalopride (R093877) and SDZ HTF-919 and the 5-HT4 receptor agonists cisapride and 5-MeOT relaxed the muscle strips with a rank order of potency R076186 = 5-HT > cisapride > prucalopride > or = SDZ HTF-919 > 5-MeOT. The selective 5-HT4 receptor antagonists GR 125487, RS 39604 and GR 113808 competitively antagonized the relaxations to 5-HT, yielding pK(B) estimates of 9.7, 7.9 and 9.1, respectively. The selective 5-HT4 receptor antagonist SB 204070 shifted the curve to 5-HT rightward and depressed the maximal response (apparent pA2 10.6). GR 113808 (10 nM) produced a parallel rightward shift of the curve to the selective 5-HT4 receptor agonists R076186 (pA2 8.8). It is concluded that 5-HT induces relaxation of the canine rectum circular muscle through stimulation of a single population of smooth muscle 5-HT4 receptors. For the first time, a nonhuman species was shown to exhibit relaxant 5-HT4 receptors in the large intestine.
Figures



References
-
- BAXTER G.S., CRAIG D.A., CLARKE D.E. 5-Hydroxytryptamine4 receptors mediate relaxation of the rat oesophageal tunica muscularis mucosae. Naunyn-Schmiedebergs' Arch. Pharmacol. 1991;343:439–446. - PubMed
-
- BINGHAM S., KING B.F., RUSHANT B., SMITH M.I., GASTER L., SANGER G.J. Antagonism by SB 204070 of 5-HT-evoked contractions in the dog stomach: an in-vivo model of 5-HT4 receptor function. J. Pharm. Pharmacol. 1995;47:219–222. - PubMed
-
- BLONDEL O., GASTINEAU M., DAHMOUNE Y., LANGLOIS M., FISCHMEISTER R. Cloning, expression, and pharmacology of four human 5-hydroxytryptamine4 receptor isoforms produced by alternative splicing in the carboxyl terminus. J. Neurochem. 1998;70:2252–2261. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

