Influence of CGRP (8-37), but not adrenomedullin (22-52), on the haemodynamic responses to lipopolysaccharide in conscious rats
- PMID: 10455317
- PMCID: PMC1566161
- DOI: 10.1038/sj.bjp.0702718
Influence of CGRP (8-37), but not adrenomedullin (22-52), on the haemodynamic responses to lipopolysaccharide in conscious rats
Abstract
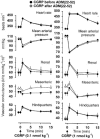
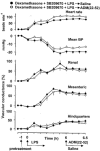
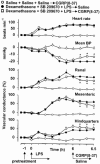
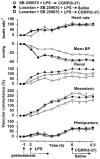
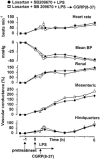
1. The functional involvement of the vasodilator peptides, adrenomedullin (ADM) and calcitonin gene-related peptide (CGRP), in the haemodynamic sequelae of continuous infusion of lipopolysaccharide (LPS) was assessed in conscious, male, Long Evans rats, by the use of peptide antagonists. 2. It was demonstrated that ADM (22-52) at a dose of 500 nmol kg-1 h-1 caused significant inhibition of the effects of ADM (1 nmol kg-1), without affecting responses to CGRP (0.1 or 1 nmol kg-1). 3. Even when the regional vasodilator responses to LPS infusion were enhanced (by pre-treatment with dexamethasone and the endothelin antagonist, SB 209670, or by pretreatment with SB 209670 and the AT1-receptor antagonist, losartan), ADM (22-52) had no significant cardiovascular effects. In contrast, the CGRP1-receptor antagonist, CGRP (8-37), caused small, but significant, inhibitions of the hypotensive and renal and mesenteric vasodilator effects of LPS, but only 6 h after onset of infusion in the presence of dexamethasone and SB 209670. 4. The results indicate that, in this model of endotoxaemia, the marked regional vasodilatations seen in the presence of dexamethasone and SB 209670 do not involve ADM, but do involve CGRP, albeit only to a small extent.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Regional haemodynamic responses to infusion of lipopolysaccharide in conscious rats: effects of pre- or post-treatment with glibenclamide.Br J Pharmacol. 1999 Dec;128(8):1772-8. doi: 10.1038/sj.bjp.0702985. Br J Pharmacol. 1999. PMID: 10588933 Free PMC article.
-
Effects of dexamethasone and SB 209670 on the regional haemodynamic responses to lipopolysaccharide in conscious rats.Br J Pharmacol. 1996 May;118(1):141-9. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1996.tb15377.x. Br J Pharmacol. 1996. PMID: 8733587 Free PMC article.
-
Temporal differences between the involvement of angiotensin II and endothelin in the cardiovascular responses to endotoxaemia in conscious rats.Br J Pharmacol. 1996 Dec;119(8):1619-27. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1996.tb16081.x. Br J Pharmacol. 1996. PMID: 8982510 Free PMC article.
-
Regional haemodynamic effects of human and rat adrenomedullin in conscious rats.Br J Pharmacol. 1995 Feb;114(3):584-91. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1995.tb17179.x. Br J Pharmacol. 1995. PMID: 7735684 Free PMC article.
-
Calcitonin gene-related peptide: vasoactive effects and potential therapeutic role.Gen Pharmacol. 1996 Jun;27(4):607-11. doi: 10.1016/0306-3623(95)00125-5. Gen Pharmacol. 1996. PMID: 8853291 Review.
Cited by
-
Inhibition of the renin-angiotensin system affects kidney tissue oxygenation evaluated by magnetic resonance imaging in patients with chronic kidney disease.J Clin Hypertens (Greenwich). 2014 Mar;16(3):214-8. doi: 10.1111/jch.12263. Epub 2014 Feb 20. J Clin Hypertens (Greenwich). 2014. PMID: 24708383 Free PMC article.
-
Mechanisms involved in the regional haemodynamic effects of intermedin (adrenomedullin 2) compared with adrenomedullin in conscious rats.Br J Pharmacol. 2009 Aug;157(8):1502-13. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.2009.00306.x. Br J Pharmacol. 2009. PMID: 19681873 Free PMC article.
-
A comparative study of the ability of calcitonin gene-related peptide and adrenomedullin(13 - 52) to modulate microvascular but not thermal hyperalgesia responses.Br J Pharmacol. 2000 Aug;130(7):1589-96. doi: 10.1038/sj.bjp.0703502. Br J Pharmacol. 2000. PMID: 10928962 Free PMC article.
-
Regional haemodynamic responses to infusion of lipopolysaccharide in conscious rats: effects of pre- or post-treatment with glibenclamide.Br J Pharmacol. 1999 Dec;128(8):1772-8. doi: 10.1038/sj.bjp.0702985. Br J Pharmacol. 1999. PMID: 10588933 Free PMC article.
-
CGRP receptors mediating CGRP-, adrenomedullin- and amylin-induced relaxation in porcine coronary arteries. Characterization with 'Compound 1' (WO98/11128), a non-peptide antagonist.Br J Pharmacol. 2001 Aug;133(8):1405-13. doi: 10.1038/sj.bjp.0704210. Br J Pharmacol. 2001. PMID: 11498528 Free PMC article.
References
-
- ARDEN W.A., FISCUS R.R., WANG X., YANG L., MALEY R., NIELSEN M., LANZO S., GROSS D.R. Elevations in circulating calcitonin gene-related peptide correlate with hemodynamic deterioration during endotoxic shock in pigs. Circ. Shock. 1994;42:147–153. - PubMed
-
- CHAMPION H.C., FRIEDMAN D.E., LAMBERT D.G., MURPHY W.A., COY D.H., KADOWITZ P.J. Adrenomedullin (16-31) has pressor activity in the rat but not the cat. Peptides. 1997b;18:133–136. - PubMed
-
- CHAMPION H.C., FRY R.C., MURPHY W.A., COY D.H., KADOWITZ P.J. Catecholamine release mediates pressor effects of adrenomedullin-(15-22) in the rat. Hypertension. 1996;28:1041–1046. - PubMed
-
- CHAMPION H.C., SANTIAGO J.A., MURPHY W.A., COY D.H., KADOWITZ P.J. Adrenomedullin-(22-52) antagonizes vasodilator responses to CGRP but not adrenomedullin in the cat. Am. J. Physiol. 1997a;272:R234–R242. - PubMed
-
- DOGAN A., SUZUKI Y., KOKETSU N., OSUKA K., SAITO K., TAKAYASU M., SHIBUYA M., YOSHIDA J. Intravenous infusion of adrenomedullin and increase in regional cerebral blood flow and prevention of ischemic brain injury after middle cerebral artery occlusion in rats. J. Cereb. Blood Flow Metab. 1997;17:19–25. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

