Fibrinogen cleavage by the Streptococcus pyogenes extracellular cysteine protease and generation of antibodies that inhibit enzyme proteolytic activity
- PMID: 10456870
- PMCID: PMC96748
- DOI: 10.1128/IAI.67.9.4326-4333.1999
Fibrinogen cleavage by the Streptococcus pyogenes extracellular cysteine protease and generation of antibodies that inhibit enzyme proteolytic activity
Abstract
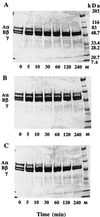
The extracellular cysteine protease from Streptococcus pyogenes is a virulence factor that plays a significant role in host-pathogen interaction. Streptococcal protease is expressed as an inactive 40-kDa precursor that is autocatalytically converted into a 28-kDa mature (active) enzyme. Replacement of the single cysteine residue involved in formation of the enzyme active site with serine (C192S mutation) abolished detectable proteolytic activity and eliminated autocatalytic processing of zymogen to the mature form. In the present study, we investigated activity of the wild-type (wt) streptococcal protease toward human fibrinogen and bovine casein. The former is involved in blood coagulation, wound healing, and other aspects of hemostasis. Treatment with streptococcal protease resulted in degradation of the COOH-terminal region of fibrinogen alpha chain, indicating that fibrinogen may serve as an important substrate for this enzyme during the course of human infection. Polyclonal antibodies generated against recombinant 40- and 28-kDa (r40- and r28-kDa) forms of the C192S streptococcal protease mutant exhibited high enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay titers but demonstrated different inhibition activities toward proteolytic action of the wt enzyme. Activity of the wt protease was readily inhibited when the reaction was carried out in the presence of antibodies generated against r28-kDa C192S mutant. Antibodies produced against r40-kDa C192S mutant had no significant effect on proteolysis. These data suggest that the presence of the NH(2)-terminal prosegment prevents generation of functionally active antibodies and indicate that inhibition activity of antibodies most likely depends on their ability to bind the active-site region epitope(s) of the protein.
Figures



References
-
- Bilezikian S B, Nossel H L. Unique pattern of fibrinogen cleavage by human leukocyte proteases. Blood. 1977;50:21–28. - PubMed
-
- Corbett S A, Lee L, Wilson C L, Schwarzbauer J E. Covalent cross-linking of fibronectin to fibrin is required for maximal cell adhesion to a fibronectin-fibrin matrix. J Biol Chem. 1997;272:24999–25005. - PubMed
-
- Cottrell B A, Strong D D, Watt K W K, Doolittle R F. Amino acid sequence studies on the α chain of human fibrinogen. Exact location of cross-linking acceptor sites. Biochemistry. 1979;18:5405–5410. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

