Genetically detoxified mutants of heat-labile toxin from Escherichia coli are able to act as oral adjuvants
- PMID: 10456880
- PMCID: PMC96758
- DOI: 10.1128/IAI.67.9.4400-4406.1999
Genetically detoxified mutants of heat-labile toxin from Escherichia coli are able to act as oral adjuvants
Abstract
Detoxified mutants of the Escherichia coli heat-labile toxin (LT) act as mucosal adjuvants to intranasally presented coadministered antigens. Here, we compare the adjuvant activity of a panel of detoxified derivatives of LT, using both intranasal (i.n.) and oral (p.o.) routes of administration. The mutants used as adjuvants varied in sensitivity to proteases and toxicity. With keyhole limpet hemocyanin (KLH) as the bystander antigen, the immune responses to i. n. immunizations were consistently higher than the equivalent p.o. -delivered proteins. LT-G192, a mutant which demonstrates a 10-fold reduction in toxicity in vitro, demonstrated wild-type adjuvant activity both i.n. and p.o., inducing similar titers of KLH specific antibody in the sera and immunoglobulin A in local mucosal secretions as wild-type LT. In line with previous data, the nontoxic holotoxoid LT-K63 induced intermediate immune responses in both the serum and mucosal secretions which were lower than those achieved with wild-type LT but at least 10-fold higher than those measured when the antigen was administered with LT-B. Although significant levels of local and systemic anti-KLH antibodies were induced following p.o. immunization with LT-K63, cellular proliferative responses to KLH was poor or undetectable. In contrast, LT and LT-G192 induced significant T-cell responses to KLH following p.o. immunization. These proliferating cells secreted both gamma interferon and interleukin-5, suggesting that the type of immune response induced following p.o. coimmunization with LT and purified protein is a mixed Th1/Th2 response.
Figures
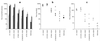
 ), 34 (■), and 49 (
), 34 (■), and 49 ( ). The results are mean titers calculated from individual animals. Error bars represent the standard deviation of the mean response. (b) Variation in individual titers of KLH specific antibody in the sera of mice at a single time point on day 49. (c) Mean IgA response detected in the lung lavage samples from these mice on day 49. Bar represent mean titers for each group.
). The results are mean titers calculated from individual animals. Error bars represent the standard deviation of the mean response. (b) Variation in individual titers of KLH specific antibody in the sera of mice at a single time point on day 49. (c) Mean IgA response detected in the lung lavage samples from these mice on day 49. Bar represent mean titers for each group.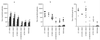
 ), 34 (■), and 49 (
), 34 (■), and 49 ( ). The results are mean titers calculated from individual animals. Error bars represent standard deviations of the mean responses. (b) Variation in individual titers of KLH-specific antibody in sera of mice on day 49. (c) Titers of KLH-specific IgA from intestinal washes from individual animals on day 49. Limited intestinal samples were available for testing from groups immunized with LT-G192 or LT-K63/G192.
). The results are mean titers calculated from individual animals. Error bars represent standard deviations of the mean responses. (b) Variation in individual titers of KLH-specific antibody in sera of mice on day 49. (c) Titers of KLH-specific IgA from intestinal washes from individual animals on day 49. Limited intestinal samples were available for testing from groups immunized with LT-G192 or LT-K63/G192.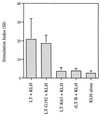
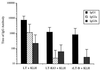
 ), and IgG2b (▨) were calculated from at least eight mice per group. Error bars represent standard deviations of the mean responses.
), and IgG2b (▨) were calculated from at least eight mice per group. Error bars represent standard deviations of the mean responses.Similar articles
-
Mutational analysis of the role of ADP-ribosylation activity and GM1-binding activity in the adjuvant properties of the Escherichia coli heat-labile enterotoxin towards intranasally administered keyhole limpet hemocyanin.Eur J Immunol. 1998 Apr;28(4):1243-50. doi: 10.1002/(SICI)1521-4141(199804)28:04<1243::AID-IMMU1243>3.0.CO;2-E. Eur J Immunol. 1998. PMID: 9565364
-
Modulation of innate and acquired immune responses by Escherichia coli heat-labile toxin: distinct pro- and anti-inflammatory effects of the nontoxic AB complex and the enzyme activity.J Immunol. 2000 Nov 15;165(10):5750-9. doi: 10.4049/jimmunol.165.10.5750. J Immunol. 2000. PMID: 11067933
-
Clostridium difficile toxin A carboxyl-terminus peptide lacking ADP-ribosyltransferase activity acts as a mucosal adjuvant.Infect Immun. 2004 May;72(5):2827-36. doi: 10.1128/IAI.72.5.2827-2836.2004. Infect Immun. 2004. PMID: 15102793 Free PMC article.
-
A proposal for safety standards for human use of cholera toxin (or Escherichia coli heat-labile enterotoxin) derivatives as an adjuvant of nasal inactivated influenza vaccine.Jpn J Infect Dis. 2000 Jun;53(3):98-106. Jpn J Infect Dis. 2000. PMID: 10957706 Review.
-
Mutants of the Escherichia coli heat-labile enterotoxin as safe and strong adjuvants for intranasal delivery of vaccines.Expert Rev Vaccines. 2003 Apr;2(2):285-93. doi: 10.1586/14760584.2.2.285. Expert Rev Vaccines. 2003. PMID: 12899578 Review.
Cited by
-
Novel approaches to vaccine delivery.Pharm Res. 2004 Sep;21(9):1519-30. doi: 10.1023/b:pham.0000041443.17935.33. Pharm Res. 2004. PMID: 15497674 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Humoral immune and adjuvant responses of mucosally-administered Tinospora cordifolia immunomodulatory protein in BALB/c mice.J Ayurveda Integr Med. 2020 Apr-Jun;11(2):140-146. doi: 10.1016/j.jaim.2017.10.006. Epub 2018 Nov 17. J Ayurveda Integr Med. 2020. PMID: 30455069 Free PMC article.
-
Construction and characterization of bivalent Shigella flexneri 2a vaccine strains SC608(pCFAI) and SC608(pCFAI/LTB) that express antigens from enterotoxigenic Escherichia coli.Infect Immun. 2005 Jan;73(1):258-67. doi: 10.1128/IAI.73.1.258-267.2005. Infect Immun. 2005. PMID: 15618162 Free PMC article.
-
Attenuated Shigella flexneri 2a vaccine strain CVD 1204 expressing colonization factor antigen I and mutant heat-labile enterotoxin of enterotoxigenic Escherichia coli.Infect Immun. 2000 Sep;68(9):4884-92. doi: 10.1128/IAI.68.9.4884-4892.2000. Infect Immun. 2000. PMID: 10948101 Free PMC article.
-
Transcutaneous immunization with bacterial ADP-ribosylating exotoxins, subunits, and unrelated adjuvants.Infect Immun. 2000 Sep;68(9):5306-13. doi: 10.1128/IAI.68.9.5306-5313.2000. Infect Immun. 2000. PMID: 10948159 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Clements J D, Hartzog N M, Lyon F L. Adjuvant activity of Escherichia coli heat labile enterotoxin and effect of induction of oral tolerance in mice to unrelated antigens. Vaccine. 1988;6:269–277. - PubMed
-
- de Haan L, Feil I K, Verweij W R, Holtrop M, Hol W G, Agsteribbe E, Wilschut J. Mutational analysis of the role of ADP-ribosylation activity and GM1-binding activity in the adjuvant properties of the Escherichia coli heat-labile enterotoxin towards intranasally administered keyhole limpet hemocyanin. Eur J Immunol. 1998;28:1243–1250. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

