Binding of rat and human surfactant proteins A and D to Aspergillus fumigatus conidia
- PMID: 10456901
- PMCID: PMC96779
- DOI: 10.1128/IAI.67.9.4563-4569.1999
Binding of rat and human surfactant proteins A and D to Aspergillus fumigatus conidia
Abstract
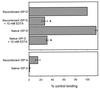
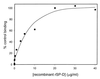
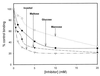
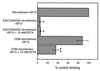
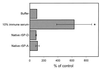
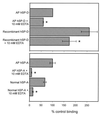
Surfactant proteins A (SP-A) and D (SP-D) are thought to play important roles in pulmonary host defense. We investigated the interactions of rat and human SP-A and SP-D with Aspergillus fumigatus conidia. Rat SP-D but not rat SP-A bound the conidia, and the binding was inhibited by EDTA, mannose, glucose, maltose, and inositol. Binding studies using a mutant recombinant rat SP-D with altered carbohydrate recognition but normal structural organization clearly established a role for the carbohydrate recognition domain in binding to conidia. However, neither rat SP-A nor SP-D increased the association of fluorescein isothiocyanate-labeled conidia with rat alveolar macrophages as determined by flow cytometry. Both human SP-A (isolated from normal and alveolar proteinosis lungs) and SP-D (recombinant protein and protein isolated from alveolar proteinosis lungs) bound the conidia. These data indicate that important differences exist between rat and human SP-A in binding to certain fungi. Human SP-A and SP-D binding to conidia was also examined in the presence of hydrophobic surfactant components (HSC), containing both the phospholipid and hydrophobic proteins of surfactant. We found that HSC inhibited but did not eliminate human SP-A binding to Aspergillus conidia. In contrast, the SP-D binding to conidia was unaffected by HSC. These findings indicate that SP-D plays a major role in the recognition of Aspergillus conidia in alveolar fluid.
Figures

References
-
- Allen M, Mason R, Harbeck R, Greene K, Smith B, Voelker D. Abstracts of the 1998 International Conference of the American Thoracic Society. Am. J. Respir. Crit. Care Med. 157:A865. 1998. Binding of rat SP-A and SP-D to Aspergillus spores.
-
- Benne C A, Benaissa-Trouw B, van Strijp J A, Kraaijeveld C A, van Iwaarden J F. Surfactant protein A, but not surfactant protein D, is an opsonin for influenza A virus phagocytosis by rat alveolar macrophages. Eur J Immunol. 1997;27:886–890. - PubMed
-
- Benne C A, Kraaijeveld C A, van Strijp J A, Brouwer E, Harmsen M, Verhoef J, van Golde L M, van Iwaarden J F. Interactions of surfactant protein A with influenza A viruses: binding and neutralization. J Infect Dis. 1995;171:335–341. - PubMed
-
- Crouch E C. Collectins and pulmonary host defense. Am J Respir Cell Mol Biol. 1998;19:177–201. - PubMed
-
- Hartshorn K, Chang D, Rust K, White M, Heuser J, Crouch E. Interactions of recombinant human pulmonary surfactant protein D and SP-D multimers with influenza A. Am J Physiol. 1996;271:L753–L762. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

