Biophysical properties of mouse connexin30 gap junction channels studied in transfected human HeLa cells
- PMID: 10457079
- PMCID: PMC2269545
- DOI: 10.1111/j.1469-7793.1999.0631n.x
Biophysical properties of mouse connexin30 gap junction channels studied in transfected human HeLa cells
Abstract
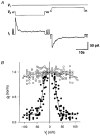
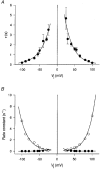
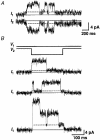
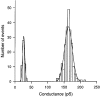
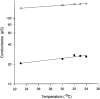
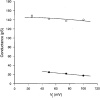
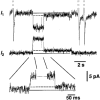
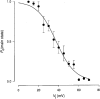
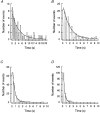
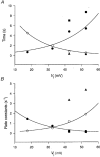
1. Human HeLa cells expressing mouse connexin30 (Cx30) were used to study the electrical properties of Cx30 gap junction channels. Experiments were performed on cell pairs with the dual voltage-clamp method. 2. The gap junction conductance (gj) at steady state showed a bell-shaped dependence on junctional voltage (Vj; Boltzmann fit: Vj,0 = 27 mV, gj,min = 0.15, z = 4). The instantaneous gj decreased slightly with increasing Vj. 3. The gap junction currents (Ij) declined with time following a single exponential. The time constants of Ij inactivation (taui) decreased with increasing Vj. 4. Single channels exhibited a main state, a residual state and a closed state. The conductances gammaj,main and gammaj,residual were 179 and 48 pS, respectively (pipette solution, potassium aspartate; temperature, 36-37 degrees C; extrapolated to Vj = 0 mV). 5. The conductances gammaj,residual and gammaj,main showed a slight Vj dependence and were sensitive to temperature (Q10 values of 1.28 and 1.16, respectively). 6. Current transitions between open states (i.e. main state, substates, residual state) were fast (< 2 ms), while those between an open state and the closed state were slow (12 ms). 7. The open channel probability (Po) at steady state decreased from 1 to 0 with increasing Vj (Boltzmann fit: Vj,0 = 37 mV; z = 3). 8. Histograms of channel open times implied the presence of a single main state; histograms of channel closed times suggested the existence of two closed states (i.e. residual states). 9. We conclude that Cx30 channels are controlled by two types of gates, a fast one responsible for Vj gating involving transitions between open states (i.e. residual state, main state), and a slow one correlated with chemical gating involving transitions between the closed state and an open state.
Figures

Similar articles
-
The electrical behaviour of rat connexin46 gap junction channels expressed in transfected HeLa cells.Pflugers Arch. 2003 Sep;446(6):714-27. doi: 10.1007/s00424-003-1129-5. Epub 2003 Jul 12. Pflugers Arch. 2003. PMID: 12861414
-
Biophysical properties of gap junction channels formed by mouse connexin40 in induced pairs of transfected human HeLa cells.Biophys J. 1995 Jun;68(6):2289-98. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(95)80411-X. Biophys J. 1995. PMID: 7544165 Free PMC article.
-
Voltage dependence of macroscopic and unitary currents of gap junction channels formed by mouse connexin50 expressed in rat neuroblastoma cells.J Physiol. 1999 Jun 15;517 ( Pt 3)(Pt 3):673-89. doi: 10.1111/j.1469-7793.1999.0673s.x. J Physiol. 1999. PMID: 10358109 Free PMC article.
-
Emerging issues of connexin channels: biophysics fills the gap.Q Rev Biophys. 2001 Aug;34(3):325-472. doi: 10.1017/s0033583501003705. Q Rev Biophys. 2001. PMID: 11838236 Review.
-
Gating of Connexin Channels by transjunctional-voltage: Conformations and models of open and closed states.Biochim Biophys Acta Biomembr. 2018 Jan;1860(1):22-39. doi: 10.1016/j.bbamem.2017.04.028. Epub 2017 May 2. Biochim Biophys Acta Biomembr. 2018. PMID: 28476631 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Cardiac connexins Cx43 and Cx45: formation of diverse gap junction channels with diverse electrical properties.Pflugers Arch. 2004 Jul;448(4):363-75. doi: 10.1007/s00424-004-1250-0. Epub 2004 Mar 27. Pflugers Arch. 2004. PMID: 15048573
-
Dominant Cx26 mutants associated with hearing loss have dominant-negative effects on wild type Cx26.Mol Cell Neurosci. 2011 Jun;47(2):71-8. doi: 10.1016/j.mcn.2010.10.002. Epub 2010 Oct 30. Mol Cell Neurosci. 2011. PMID: 21040787 Free PMC article.
-
Intercellular communication in spinal cord astrocytes: fine tuning between gap junctions and P2 nucleotide receptors in calcium wave propagation.J Neurosci. 2000 Feb 15;20(4):1435-45. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.20-04-01435.2000. J Neurosci. 2000. PMID: 10662834 Free PMC article.
-
Altered gating properties of functional Cx26 mutants associated with recessive non-syndromic hearing loss.Hum Genet. 2004 Aug;115(3):191-9. doi: 10.1007/s00439-004-1142-6. Epub 2004 Jul 7. Hum Genet. 2004. PMID: 15241677
-
The electrical behaviour of rat connexin46 gap junction channels expressed in transfected HeLa cells.Pflugers Arch. 2003 Sep;446(6):714-27. doi: 10.1007/s00424-003-1129-5. Epub 2003 Jul 12. Pflugers Arch. 2003. PMID: 12861414
References
-
- Banach K, Weingart R. Connexin43 gap junctions exhibit asymmetrical gating properties. Pflügers Archiv. 1996;431:775–785. - PubMed
-
- Brink PR, Ramanan SV, Christ GJ. Human connexin 43 gap junction channel gating: evidence for mode shifts and/or heterogeneity. American Journal of Physiology. 1996;271:C321–331. - PubMed
-
- Bruzzone R, White TW, Paul D. Connections with connexins: the molecular basis of direct intercellular signalling. European Journal of Biochemistry. 1996;238:1–27. - PubMed
-
- Bukauskas FF, Elfgang C, Willecke K, Weingart R. Heterotypic gap junction channels (connexin26-connexin32) violate the paradigm of unitary conductance. Pflügers Archiv. 1995b;429:870–872. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

