Relationship between transient outward K+ current and Ca2+ influx in rat cardiac myocytes of endo- and epicardial origin
- PMID: 10457095
- PMCID: PMC2269536
- DOI: 10.1111/j.1469-7793.1999.0841n.x
Relationship between transient outward K+ current and Ca2+ influx in rat cardiac myocytes of endo- and epicardial origin
Abstract
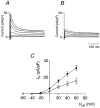
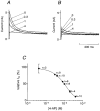
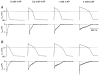
1. The transient outward K+ current (Ito) is a major repolarizing ionic current in ventricular myocytes of several mammals. Recently it has been found that its magnitude depends on the origin of the myocyte and is regulated by a number of physiological and pathophysiological signals. 2. The relationship between the magnitude of Ito, action potential duration (APD) and Ca2+ influx (QCa) was studied in rat left ventricular myocytes of endo- and epicardial origin using whole-cell recordings and the action potential voltage-clamp method. 3. Under control conditions, in response to a depolarizing voltage step to +40 mV, Ito averaged 12.1 +/- 2.6 pA pF-1 in endocardial (n = 11) and 24.0 +/- 2.6 pA pF-1 in epicardial myocytes (n = 12; P < 0.01). APD90 (90 % repolarization) was twice as long in endocardial myocytes, whereas QCa inversely depended on the magnitude of Ito. L-type Ca2+ current density was similar in myocytes from both regions. 4. To determine the effects of controlled reductions of Ito on QCa, recordings were repeated in the presence of increasing concentrations of the Ito inhibitor 4-aminopyridine. 5. Inhibition of Ito by as little as 20 % more than doubled QCa in epicardial myocytes, whereas it had only a minor effect on QCa in myocytes of endocardial origin. Further inhibition of Ito led to a progressive increase in QCa in epicardial myocytes; at 90 % inhibition of Ito, QCa was four times larger than the control value. 6. We conclude that moderate changes in the magnitude of Ito strongly affect QCa primarily in epicardial regions. An alteration of Ito might therefore allow for a regional regulation of contractility during physiological and pathophysiological adaptations.
Figures


References
-
- Agus ZS, Dukes ID, Morad M. Divalent cations modulate the transient outward current in rat ventricular myocytes. American Journal of Physiology. 1991;261:C310–318. - PubMed
-
- Allen TJ, Baker PF. Intracellular Ca indicator Quin-2 inhibits Ca2+ inflow via Na/Ca exchange in squid axon. Nature. 1985;315:755–756. - PubMed
-
- Beuckelmann DJ, Näbauer M, Erdmann E. Alterations of K+ currents in isolated human ventricular myocytes from patients with terminal heart failure. Circulation Research. 1993;73:379–385. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

